Contemporary & Hybrid Technology Monitoring Watch And Ways To Mitigate Disruption Risks
When upcoming technologies are forecasted to do well in the immediate future, most businesses are intrigued, and they want to invest in that technology or advance the product further. However, as technologies move past their innovation stage and are actually ready for market expansion, the right time to start on the technology is lost, which is typically when research was published, and patent applications were being filed. This reflects a loss for the businesses who wished to invest in the innovation and reap benefits. To avoid such a scenario and to not lose advantage over evolving trends, regular technology monitoring is required. Hybrid technology monitoring is a contemporary study, which is advantageous over traditional monitoring.
Table of Contents
Hybrid Technology Monitoring
Hybrid Technology Monitoring is an amalgamation of tracking key indicators: patents, non-patent literature and markets to gain competitive advantage.
Why Hybrid Searches?
Hybrid monitoring is beneficial than traditional monitoring since it covers complimentary information from all the three indicators together. The information from one source is substantiated from the corresponding source and thus, removes chances of false positives in the study. To illustrate, the study can provide information related to key companies active in R&D (identified from patent analysis) as well as commercialization (identified from market and non-patent information). The study provides information related to patent infringement, leading geographies, markets and players collectively with continuous updates in a regular interval. This enables comparative mapping on all the three aspects – to hack growth avenues and future strategies of competitors.
Key Indicators in Detail
Key indications from patent analysis can provide the following information:
- Competing Technologies
- Untapped Potential
- Crucial Geographies
- Legal Scope & Status
Key indications from non-patent analysis can provide the following information:
- Ongoing Research in the technology domain where the patents are not filed
- Patented Technology translated into products
- Key grant agencies, researchers
- Product infringements on patents
Indications from Markets can provide the following information:
- Key Market Players
- Major markets worldwide (product wise)
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Market Threats and Competition
- Future Predictions for Growth
How to Scope the Technology Monitoring Study
Scoping means deciding what all needs to be covered in the search. The coverage can be decided, if the study is done from mega trends stage, or planning stage or others.
Various global trends that affect the technical, commercial, legal and economic aspects of a business can be studied and their impacts on the industries, demographics and consumer behaviour can be correlated to plan business strategy around a technology. Therefore, a monitoring study can be scoped at preliminary level of analysing trends, or straight away to planning stage related to R&D, funding and market outlook. The study can also be initiated when a technology is at a pilot stage or just before getting launched in the market. Technology monitoring, therefore, can be performed at any of these phases or all of these phases, starting from a broader perspective using mega trends and then narrowing down to specific niche domain as per the identified trends and insights. The phases of technical monitoring can be defined as:
Mega Trends>Planning>Pilot>Deployment
Monitoring at each of these phases is described below:
1. Technology Monitoring Mega Trends
Mega-Trends provide a global view of factors at macro-level in long-term shift that can impact the technology, business, economies, and demographics, etc. in response to consumers’ demands.
A few pointers related to recent insights on Megatrends worldwide and how they impact industries can be illustrated with Top influencing megatrends such as IT Automation, Data Cybersecurity and Green & Sustainable Tech etc. At present, Green Tech around the globe is revolutionizing different industries including Energy & Material Industries.
Insights from the Megatrends are used by businesses to strategize on evolving own products and/or technology to develop products and decide allocation of funds for R&D.
Mega trends can be identified by running searches on Global scale covering technology trends over a broad scope of industries and sectors. The search and analysis coverage is preliminary bird’s eye view and covers Global Technology Landscape Searches (Patent + NPL + Market). To add on the analysis capability, competitor and commercial monitoring can also be integrated in the study.
Key points addressed in the Mega Trends are:
- Geographical Coverage of Industries
- Top Technologies in Key Geographies
- Leading Technology classes
- Key Players in evolving industry
- Long-term (e.g. 3-5years) comparative trends across companies and industries/sectors
- Long-term (e.g. 5-year) comparative trends across Market presence and Consumer Behavior
Mega Trends analysis is presented with an exemplary case showcasing Trends influencing Material Science Industry and related sectors and sub-sectors. A global search can start off from a few related trends for the industry and corresponding sectors and sub-sectors that could be intersecting or diverging within the space.

2. Technology Monitoring during Planning Phase
Once the factors influencing global-scale trends have been identified and their implications predicted for future, the next step is to apply that knowledge in business strategies. This involves identifying key information to determine tech and application areas, which are most relevant to own business to strategize ahead.
Monitoring during this phase provides insights to plan around:
- Driving Factors behind the trends: Tech & Consumer behaviours are prominent factors apart from other socio-economic factors.
- Impact Assessment: Budgeting and investing based on quantified impact.
- Portfolio Evaluation: Evaluation and valuation of current portfolio and future course of action.
- Innovation: Determining innovation possibilities from non-traditional and converging/diverging space.
To monitor during Planning, searches are run on a global scale across industries for insights on certain technology sectors and application areas, wherein the search and analysis coverage is medium. The study involves Technology/Application Landscape Searches (Patent + NPL + Market) and may additionally include Commercial Monitoring.
Key Points addressed in the Monitoring Phase are:
- Tech distribution across Key Sectors
- Top Players across Geographies & Technologies
- Clustering potential tech and market space into comparative matrices
- Identifying parallels between existing space and unexplored areas
- Determining Cross-domain functionalities and applications categories with moderate proportion of filings and whitespace
Developing on the above exemplary case, a few trends relevant for a business in Material Industry can be narrowed down along with limiting intersecting and related sectors. At this stage, some trends not aligning with the business and tech objective can be eliminated from the analysis.
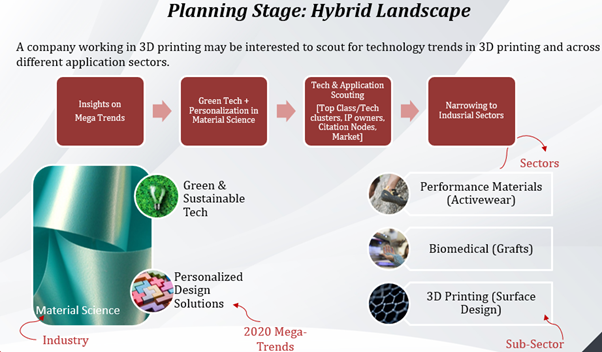
Accordingly, the business can proceed forward implementing Green and Sustainable Tech and Personalized Solutions to their technology as per the insights drawn from monitoring performed at Planning Stage. The sectors of interest in accordance with the tech and application area are also limited at this point.
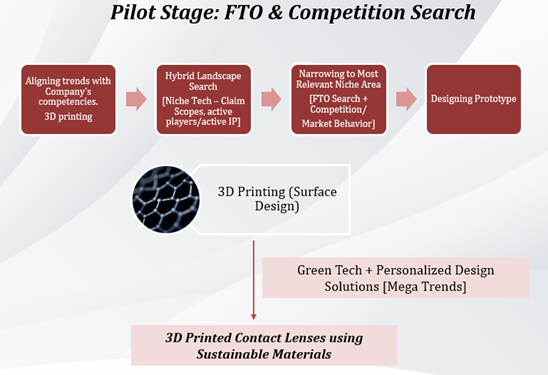
3.Technology Monitoring during Pilot Phase
Actionable insights from previous stages are validated by a Pilot study. This is a check to confirm whether the benefits outweigh the challenges. Insights from Pilot-phase Monitoring are used by businesses in identifying bottlenecks or initial problems in their technology. The technology can be put up for validation and tests before deciding scale-up and future roadmap. The information can be further useful in deciding cost competence and success of a technology, whether integration of the technology is feasible in current systems and if there are possibilities of easy user adoption. Another important factor to consider is duration between running pilot phase and scale-up.
To monitor during Pilot phase, searches are run to specifically capture overlapping key features and functional aspects of the technology. Search and analysis coverage is narrow and includes FTO/Clearance Searches, Novelty Searches and Commercial Monitoring (chances of inadvertently infringing a competitor).
Key Points addressed in this Phase:
- Identifying technology groups and categories with niche filings and whitespace
- Determining incubation, partnership, and licensing opportunities
Further, narrowing down to technology of interest, based on FTO and market analysis, a prototype can be decided. The prototype can include the trends and tech that are most aligned with the business.
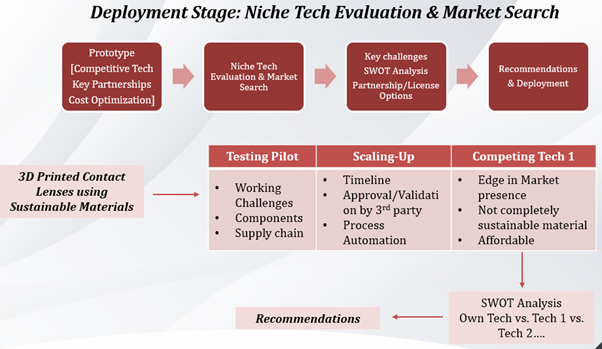
4. Technology Monitoring During Deployment Phase
This phase involves scaling up from pilot phase to commercially viable and sustainable business model. Monitoring at Deployment phase provides insights on market and consumer trends, clearance or go-ahead for the technology launch and third-party competition strategies. Other parameters crucial to understanding such as performance indicators and scope for upgrade and commercialization or technology transfer support information, can also be determined.
To monitor during Deployment phase, searches are run to determine commercial feasibility of the product, expansion opportunities and market presence despite competition. The search and analysis is highly specific and includes Tech and Market Evaluation, SWOT Analysis and detailed evaluation on risks & opportunities.
Key Points addressed in this case
- Technology/product clearance
- Performance Indicators: Tech benchmarking
- Litigation, representatives, partnerships, and license information
- Regulatory limitations
Setting Up Technology Monitoring – What all to be considered
Setting up monitoring depends on the phase of technology growth and development. It is further decided as per the business objectives, whether there are some details that need to be reviewed before moving on to the next phase, etc. Key considerations related to insights that a business is striving for and optimum timelines to generate those insights are as follows:
Monitoring Patents for Landscapes, Freedom to Operate — Quarterly/Biannually
Insights:
- Classification Clusters
- Tech vs. Competitors
- Tech vs. Geographies
- Competitor vs. Geographies
- Leading Industries/Sectors
- Competitors vs. Citations
Monitoring Literature for Landscape, Infringement— Monthly/Quarterly
Insights:
- Technologies not patented
- Individual inventors/research institutes active in the domain
- Tech Disclosures of Commercial Products
Monitoring Markets for News, Trends, Market Players — Monthly/Quarterly
Insights:
- Due Diligence
- Infringement Identification
- Details of Mergers and Acquisitions
How is the Information Used?
The outcome of various Monitoring searches can be used as actionable information, wherein IP can contribute to business decisions. This information can be used as IP intelligence for industry wise analysis, which is not limited to just competitors. Intelligence related to key aligning sectors and active players, which may contribute to the business in future can be obtained. Similarly, intel related to intersecting sectors and players, which cite from own IP can be used to strategize ahead. Further, this includes identifying disruption before technology percolates into the market – first mover advantage and removing false positives from actual disruption.
Such IP intelligence can address the following objectives of a business:
Risk Mitigation: Tracking competing technologies, licenses and partnerships, safeguarding from Infringement risks and decisions on developing vs. purchasing.
Strategizing for R&D: Assessing competencies & prioritizing, deciding investments/grants. This further involves tracking growth of supply chain entities at various stages and cost optimization.
Commercialization Approaches: Tracking competing technologies, licenses and partnerships. This further includes designing business solutions as per assessment on market percolation and consumer behaviours.
Tracking IP (Own/Competitor): Focusing on dominant/core tech or expanding to intersecting tech. Patent Grant rate success, monitoring & fine-tuning IP and determining emerging players or new entrants.
Building IP: Identifying expansion opportunities, fine-tuning IP & monitoring future predictions, enforcing IP and working on Patent Pools and Mergers & Acquisitions.
Conclusion
Technology is way past its disruption stage after percolating into the markets and monitoring Technical Space is crucial to prevent risks coming from untracked disruptions for any entity working in the Tech Sector. A continuous and hybrid approach covering all stages of innovation and scoping from a broad perspective and narrowing to specific strategy – is essential to achieve any of the five business objectives of interest (i.e. Risk Mitigation, Strategizing R&D, Commercialization Strategy, Tracking IP and Building IP).
-Devika Saini (Life Sciences) and the Editorial Team