The Growing Synergy Between Industrial IoT and Cloud Computing
IoT and cloud computing are transforming industrial operations by seamlessly connecting devices such as sensors, actuators, controllers, and industrial PCs into a unified network. The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) leverages these technologies to enable real-time data flow and analytics, enhancing efficiency across industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation. Traditionally, industrial automation depended on edge computing, which required on-site setup, maintenance, and management. However, businesses are increasingly shifting to cloud-based solutions, recognizing their superior scalability, accessibility, and operational advantages over traditional edge computing.
Why the cloud? Industries generate massive volumes of data that demand scalable storage and instant accessibility, precisely what cloud computing delivers. IIoT gathers data from field devices and transfers it to cloud platforms. This creates opportunities for advanced analytics and improved decision-making. Together, IIoT and cloud computing form a powerful synergy, enabling industries to enhance operations, optimize resources, and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape. This blend of innovation not only improves productivity but also lays the foundation for smarter, data-driven industrial ecosystems.
All in all, Cloud computing supercharges the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) by providing the computing power needed for AI and automation.
Table of Contents
How Cloud Computing Works in IIoT
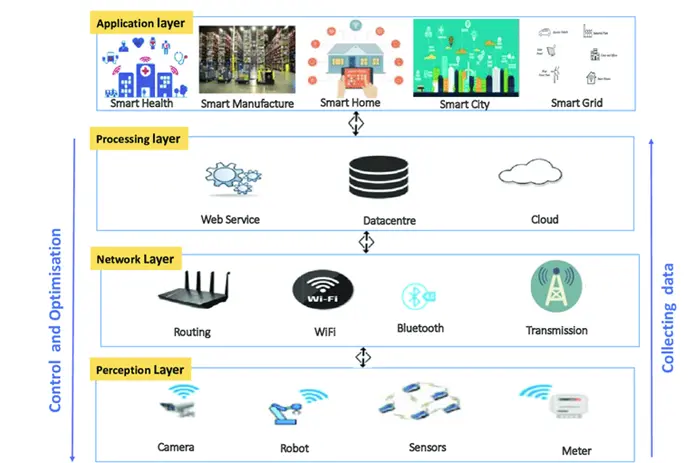
The functioning of cloud computing in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is best understood through its four-layer architecture: perception, network, processing, and application. Each layer plays a critical role in enabling seamless automation and analytics.
- Perception Layer: This is where it all begins. Sensors, actuators, and other devices gather data from industrial processes, monitoring everything from temperature and pressure to machinery performance.
- Network Layer: The collected data travels through resolute IIoT devices to the cloud. Thus, it forms the bridge between physical systems and the digital domain.
- Processing Layer: Once in the cloud, the data undergoes advanced processing and analytics. This layer ensures large-scale data storage and transforms raw information into actionable insights.
- Application Layer: Finally, user-friendly interfaces display processed data, allowing stakeholders to interpret insights, make decisions, and optimize operations effectively.
By integrating cloud computing into this structure, IIoT systems enhance efficiency, centralize data management, and provide real-time visibility into industrial processes.
Advantages of Cloud Computing in IIoT
Cloud computing plays a crucial role in advancing IIoT by offering several key benefits:
- Operational Excellence: Remote configuration and monitoring of industrial devices help detect issues early and streamline facilities management with real-time alerts from sensor data.
- Data Backup and Restoration: Cloud storage ensures easy and reliable backup and recovery of industrial data.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Users can securely access critical data from anywhere in the world with an internet connection.
- Cost Efficiency: The cloud reduces hardware and maintenance costs with a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for expensive storage infrastructure.
- Improved Collaboration: Centralized cloud platforms allow teams to access and work on shared data, fostering efficiency and teamwork.
By integrating these advantages, cloud computing helps industries optimize processes and improve overall efficiency.
Application Areas of Cloud Computing in IIoT
Cloud computing enhances the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) by optimizing processes and enabling smarter operations across industries. Key application areas include:
- Data Storage and Management: Cloud platforms provide scalable storage for the massive data generated by industrial processes, eliminating the need for costly on-premises infrastructure. Moreover, they allow seamless data mobility from multiple devices onto centralized servers, ensuring efficient analysis and secure storage of sensitive information.
- Data Analytics and Reporting: Sophisticated analytics tools in the cloud enable real-time insights using predictive modeling, statistical analysis, and machine learning. So, these insights drive informed decisions, improve efficiency, and allow for actionable reporting through dashboards and visualizations.
- Data Security: Cloud-based IIoT ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data with robust security measures, protecting sensitive information from cyber threats while complying with industry regulations.
- Automatic Software Updates: Service providers handle critical updates and backups, ensuring systems remain secure and functional without manual intervention.
- Real-Time Alerts: Cloud-based systems monitor industrial processes, issuing instant notifications for anomalies. As a result, this enables faster troubleshooting and prevents potential damage, improving operational reliability.
By integrating these functionalities, cloud computing empowers IIoT systems to optimize industrial operations, enhance decision-making, and maintain security in dynamic environments.
IP Trends
We conducted an in-depth study to examine the intellectual property (IP) landscape of Cloud Computing in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Specifically, the research focuses on identifying key companies actively filing patents in this domain. Furthermore, it highlights industry trends and technological advancements shaping this emerging field.
By analyzing patent filing patterns, we aimed to reveal insights into the competitive landscape and identify leading innovators in Cloud Computing for IIoT. The study highlights the increasing importance of intellectual property protection. It also shows how strategic IP management helps companies gain a competitive edge in this fast-evolving market.
This research is valuable for companies looking to navigate the complex world of IP in IIoT and emphasizes the importance of securing patents to safeguard innovations in the Cloud Computing space.
Patent Filing Trend
The graph below shows the number of patents filed in the Cloud Computing sector within the IIoT domain from 2014 to 2024, with filings increasing each year. This trend highlights the growing importance of cloud computing in advancing IIoT technologies, as industries increasingly adopt cloud-based solutions for better connectivity, efficiency, and scalability.
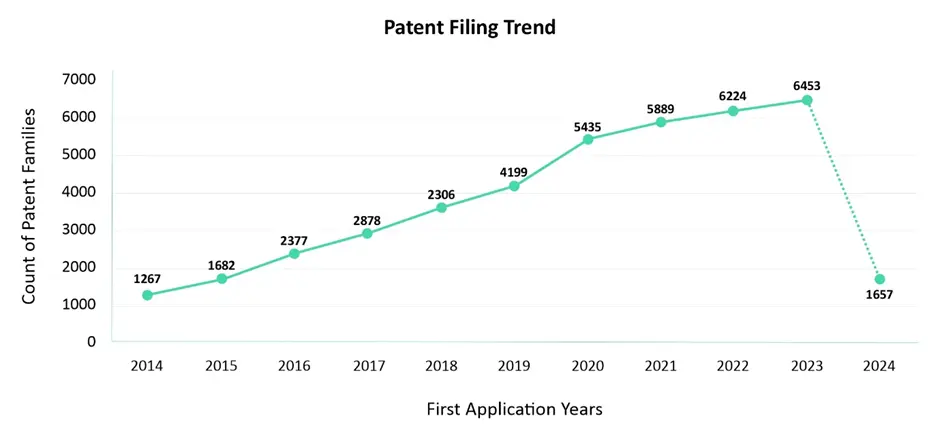
Note: Patent applications filed between 2023 and 2025 may not yet be fully published due to the 18-month publication timeline. As a result, the data may show a temporary downward trend in patent filings for this period.
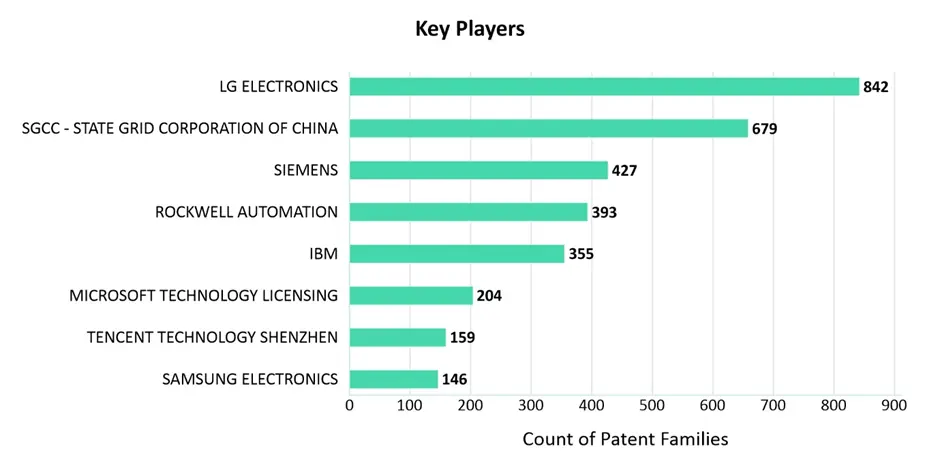
Key Players
The figure below showcases the leading patent assignees in the Cloud Computing sector within the IIoT domain. LG Electronics leads with the highest number of patents, followed by notable players such as SGCC China, Siemens, IBM, Rockwell, Microsoft, Tencent Technology, Samsung, and several others.
Let’s have a look at their market activities:
LG Electronics
It is enhancing its smart factory initiatives by integrating Digital Twin technology, big data, and generative AI. These technologies improve quality, industrial safety, and equipment management. To further this vision, the company has formed strategic partnerships, including a recent Memorandum of Understanding with LS ELECTRIC. Through this collaboration, they aim to create a Smart Factory Business Cooperation System for mutual benefit.
As part of its global strategy, LG is advancing smart factory technology by leveraging cloud computing and data analysis. In line with this, LG’s Manufacturing AI Solution team has also developed the MAVIN-Cloud platform. Powered by Google Cloud’s Anthos technology, it facilitates AI-driven quality inspections across manufacturing lines. This innovation has reduced AI model development time by over 50% and decreased false defect judgments by 95%.
State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC)
It launched a new energy cloud platform on April 20 to support China’s goal of peaking carbon dioxide emissions before 2030 and achieving carbon neutrality by 2060. The platform also aims to help build a new energy-centered power system. According to State Grid, the platform offers end-to-end services, from planning and construction to grid connection and manufacturing. It is expected to enhance scientific planning, efficient development, safe operation, and reliable energy supply.
Siemens
Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Siemens have collaborated to leverage cloud technologies for digital transformation in manufacturing. Their partnership aims to integrate industrial automation with cloud computing, enhancing the machine-to-edge and edge-to-cloud experience. Additionally, Siemens’ Industrial IoT Gateway, SIMATIC CloudConnect 7, enables reliable data transfer from S7-based devices to cloud platforms using the MQTT protocol. This enhances connectivity and improves data management.
Rockwell Automation
They launched their FactoryTalk® Design Hub platform in October 2022. This cloud-based platform is designed to enhance industrial automation design capabilities, enabling teams to collaborate more effectively and streamline their workflows.
Microsoft
Microsoft has continuously expanded its IoT offerings, introducing the Azure IoT suite and rolling out various updates over the years. The Azure IoT platform has been actively promoted since its launch. It continues to evolve with regular enhancements and new features. Its partnerships with Siemens and Rockwell further strengthen the integration of cloud services into industrial applications.
Tencent Technology
It is expanding its presence in IIoT by utilizing its cloud services to support smart manufacturing initiatives, focusing on real-time data processing and analytics.
Samsung
Samsung leverages its advanced technological expertise through the Samsung Cloud Platform to deliver innovative E2E cloud services. By integrating cutting-edge AI and data analysis, Samsung is equipped to serve a wide range of industries. These include high-tech, automotive, energy and chemicals, pharmaceuticals, distribution and consumer goods, and e-commerce. Hence, this strategic approach enables Samsung to offer tailored solutions powered by generative AI. As a result, it enhances operational efficiency and drives digital transformation across various sectors.
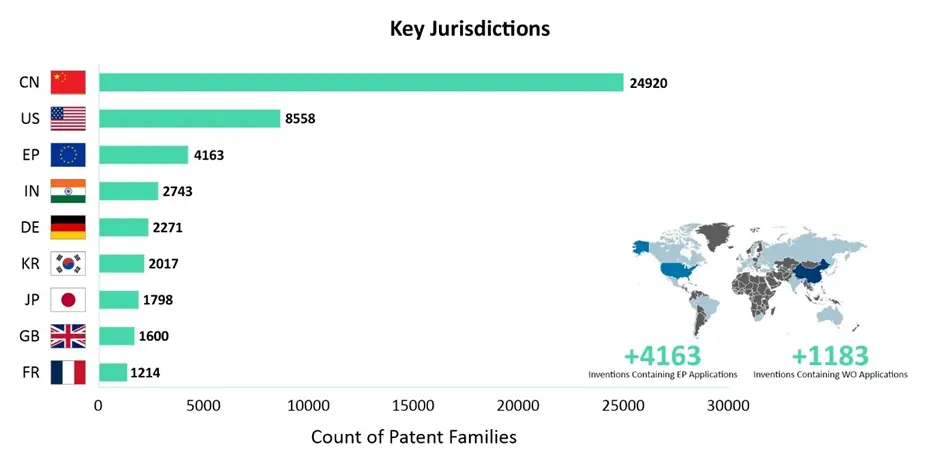
Key Jurisdictions
The figure below illustrates the number of patents filed in the Cloud Computing sector within the IIoT domain across various jurisdictions. China tops the chart, followed by the USA, Europe, India, and Germany.
Governments across key jurisdictions are driving the adoption of Cloud Computing in IIoT through strategic initiatives and funding. Notable efforts include:
China
The China Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has been pivotal in promoting IoT. It established a Special Projects Fund dedicated to advancing Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies. This fund supports various initiatives to foster innovation and infrastructure development. One key focus is the adoption of cloud computing solutions in IIoT.
In 2015, the China government launched the “Internet Plus Action Plan”, which aims to merge traditional and digital value chains across industries. Therefore, the plan aims to introduce IoT, big data, cloud computing, and mobile internet into manufacturing, retail, banking, and other traditional industries.
U.S.
The U.S. government has established public-private partnerships like the Smart Manufacturing Leadership Coalition to advance cloud-enabled IIoT technologies in manufacturing. Hence, these collaborations aim to enhance competitiveness and spur innovation within the U.S. manufacturing sector.
Europe
The European Commission is actively funding projects related to cloud computing, edge computing, and IIoT through programs such as Horizon 2020 and its successor Horizon Europe. These initiatives are designed to foster research and development across various technological domains.
Key Research Institutions
Aside from leading market players, several universities have also filed patents in the Cloud Computing sector within the IIoT domain. Among them, Beijing University of Technology leads in patent filings, followed by Zhejiang University, South China University of Technology, Southeast University, and others. The figure below highlights the top universities contributing to innovation in this field.
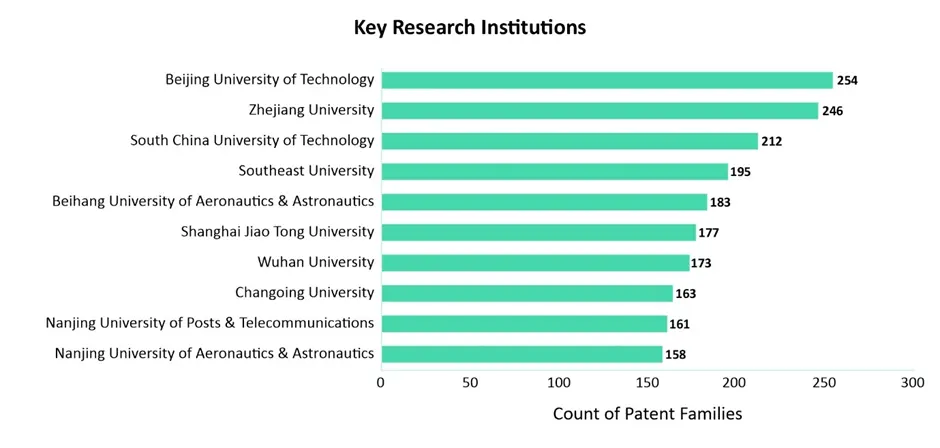
Several universities are actively collaborating with industry leaders to drive innovation in Cloud Computing for IIoT. Notable partnerships include:
- Microsoft has worked with the University of Washington on projects focused on IoT applications and smart infrastructure.
- SKF, a global leader in the bearing industry, has partnered with Ericsson and Chalmers University of Technology to enhance manufacturing processes and systems, making them faster, safer, cleaner, and more robust. This collaboration is exemplified through a pilot production system project. Additionally, this project focuses on four key demonstrators aimed at improving manufacturing system performance, increasing product quality, and enhancing manufacturing flexibility. One of the demonstrators leverages cloud services to enable data analytics, which supports predictive maintenance and decision-making processes for IIoT applications.
- IBM and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have partnered to advance AI and IoT technologies, focusing on various applications that leverage cloud computing.
- SunTech Drive has engaged with Stanford University in research targeting IIoT technologies and cloud computing solutions. Their efforts can lead to joint patent filings, particularly in the areas of device connectivity, data synchronization, and cloud services.
Market Trends
Cloud computing is reshaping the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) by offering unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and efficiency compared to traditional data centers. As IIoT adoption grows, industries generate vast volumes of data that require robust storage and processing capabilities. To address this need, cloud computing provides a transformative solution, enabling on-demand access to resources and a flexible infrastructure. Consequently, it supports diverse industrial applications, ensuring seamless data management and enhanced operational efficiency.
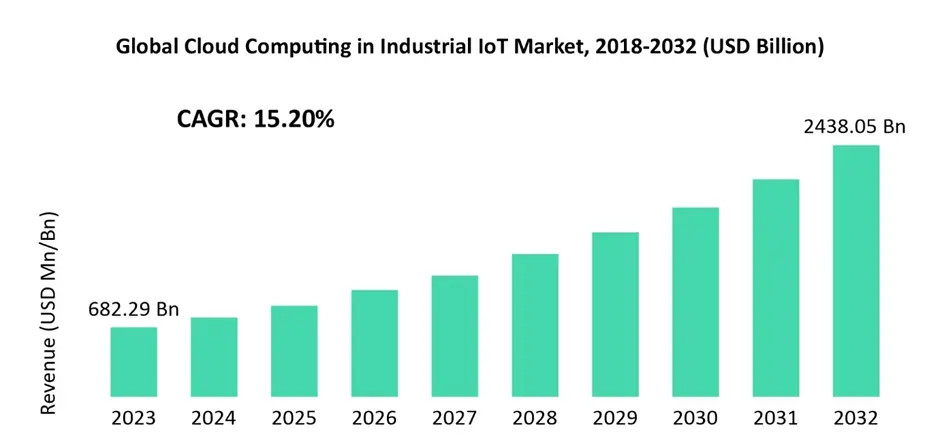
Market Trends and Projections
- Revenue Growth: In 2023, the global IIoT cloud computing market generated approximately USD 682.29 billion. This is expected to rise significantly, reaching around USD 2438.05 billion by 2032, with a 15.20% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2024 to 2032.
- Regional Leadership: By 2027, North America is projected to dominate the market, achieving a value of $93.8 billion.
- Sector Expansion
- The Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) market is expected to grow to $124.3 billion.
- The market for smart robots, driven by factory automation, is anticipated to hit $2.13 billion.
- The global demand for connected things in industrial and enterprise segments is forecasted to reach $24.1 billion by 2032.
Key Drivers of Growth
- Industrial Automation: Cloud computing is pivotal for automating processes, reducing manual intervention, and optimizing operations.
- Data-Driven Insights: The demand for real-time analytics and insights is pushing industries to adopt cloud platforms for IIoT.
- Scalability and Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models and on-demand infrastructure reduce capital expenditure while supporting scalability.
The continued expansion of cloud computing in IIoT is revolutionizing industrial processes, paving the way for smarter, data-driven, and highly automated systems.
Future of Cloud Computing in IIoT
The future of Industrial IoT and Cloud Computing looks promising, with the industry expected to reach billions—or even trillions. Cloud computing, including cloud services, big data, and data centers, is driving major computing trends. Moreover, this technology is fostering a new market paradigm, distinct from the past, and is gradually reshaping existing markets. Projections indicate significant growth for both the cloud and IIoT markets this decade. As we transition beyond the early adoption phase, mass adoption from medium-sized to small industrial automated systems is expected. Due to its on-demand nature, cloud computing offers ubiquitous access across devices, enabling real-time data and insights anytime, anywhere.
IIoT will continue to enhance productivity and operational efficiency by delivering real-time business intelligence. As a result, companies are increasingly recognizing the value of cloud adoption and the need for integration. Major industry players like Siemens, Emerson, ABB, and Rockwell have already embraced cloud technology in their automation systems. Thus, with this momentum, rapid growth is expected in the coming years. As cloud-based IIoT sees greater demand, technologies like edge computing may face reduced demand in the next decade. Moreover, given the upward trends in intellectual property filings and market growth, it is evident that cloud computing in IIoT will play an integral role in the future of industrial technology.
At Sagacious, we help businesses navigate these complexities through detailed landscape analysis, allowing you to uncover strategic opportunities in the cloud computing and IIoT sectors. By identifying key areas of growth and innovation, we empower you to make informed decisions and stay at the forefront of this rapidly advancing technological ecosystem.
• Nishant Kaushik and Lachi Chaudhary Mitthatmeer Kaur
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




