All About Trademarks in Metaverse: IP in the Virtual World
The Metaverse combines the elements of social media, online gaming, virtual reality, augmented reality, and blockchain to allow users to interact with one another using avatars. It is expected to expand in size, providing users with varied environments to play, work and socialize. Its usage is not just for people but also for brands to help them engage with their customers and market their products and services. For instance, brands can advertise in the Metaverse or even have customers browse and buy products. These virtual worlds also allow users to buy and sell branded, digital merchandise.
With the impact Metaverse could have on products and services, businesses must strive to safeguard their Intellectual Property (IP) in the Metaverse domain – especially the usage of Trademarks. Trademarking a virtual product name in the Metaverse gives the owner the exclusive rights to utilize it, prohibiting others from using a name that is the same or similar. As a result, trademark use in the Metaverse raises new legal issues, such as how to safeguard a company’s trademarks in Metaverse.
This article is a comprehensive discussion on everything you need to know about trademarks in the Metaverse, including their need, how trademarks protect brands in the Metaverse, trademark-related issues in the Metaverse, and the best practices for trademark owners, and more. Let us begin by understanding the concept of the Metaverse.
Table of Contents
How has the Metaverse evolved?
The word “Metaverse” was introduced 30 years ago by an American science fiction writer, Neal Town Stephenson, in his 1992 novel, “Snow Crash.” It was part science fiction – part speculation. Fast forward to 30 years after, this concept of an open virtual environment for everyone has become a reality. Currently, many companies are attempting to create the Metaverse or various types of mixed reality environments which combine multiple technologies, such as AI, blockchain, VR, and AR.
At a time when we are realizing the futuristic idea of the Metaverse and its essential technological innovations, one industry is leading the development of this virtual world – the gaming industry. The Metaverse is evolving from two decades of gaming and will be built upon the gaming infrastructure. Since the beginning of the Metaverse talk, game developers have been at the forefront, leading discussions on everything from virtual worlds to digital tokens.
Such is the influence of the gaming industry in the world of Metaverse that one of the prominent gaming companies, Epic Games, received its largest-ever round of fundraising with a $2 billion investment. This fundraiser has set the market capitalization of Epic Games to $31.5 billion.
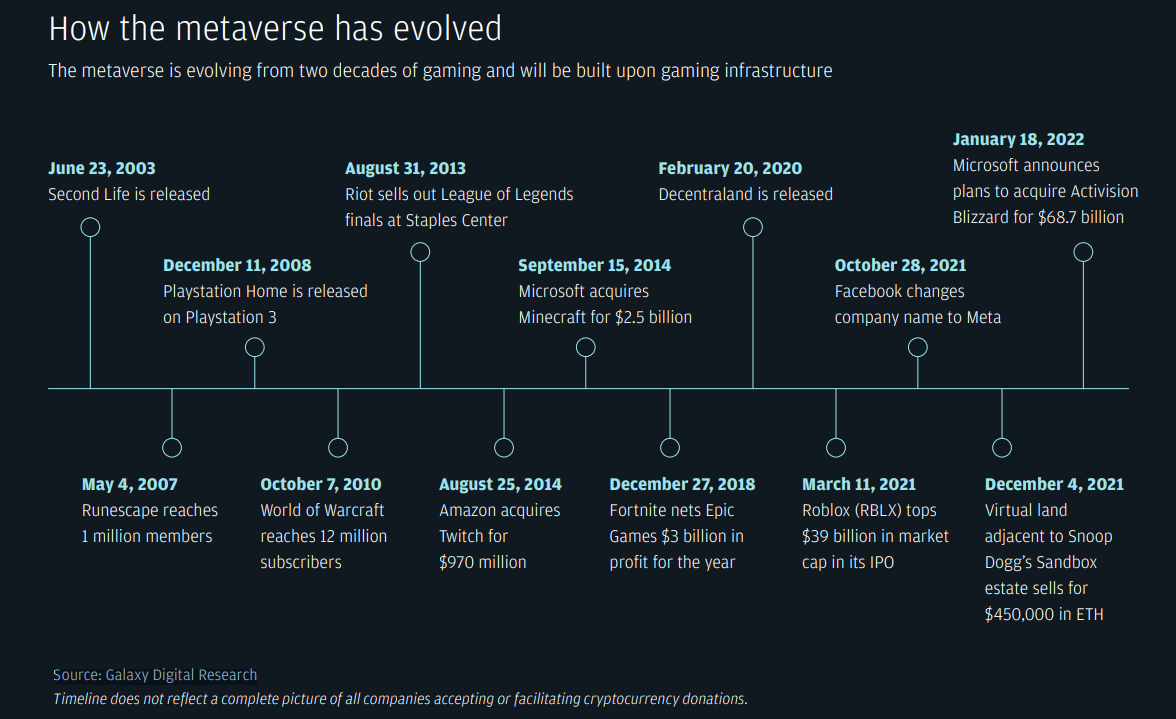
Now, let us have a look at the companies that have been leading the charge in developing the Metaverse.
Who is Developing the Metaverse?
Companies developing the Metaverse are focused on building new innovations and features to enable users to interact with each other efficiently and effectively digitally. The Metaverse companies are at the forefront of transforming the digital world with immersive experiences in the future. The top ten companies developing this digital space are:
- Meta (Previously Facebook)
- NVIDIA
- Epic Games
- Microsoft
- Apple
- Decentraland
- Roblox Corporation
- Unity Software
- Snapchat
- Amazon
Many businesses want to know more about what the Metaverse can accomplish or what their brands can do in this virtual space. The following section will explain the same.
What does the Metaverse mean for Brands?
The Metaverse is a new area for businesses to reach a wider audience, expand their digital footprint, and boost revenues. Realizing the behemoth potential here, several major brands have already started strategizing new marketing campaigns covering this new digital world. Much like the current social platforms, the Metaverse demands digital brands to carry a voice appropriate for the platform and behave a certain way depending on the type of environment.
This calls for an authentic brand image that extends into the experiences marketers create within the Metaverse. From brands’ perspective, the Metaverse is nothing but a platform to increase business digitally, just like in the real world. And trademarks are expected to help companies prevent misuse by competitors. Trademark registration for their use in the Metaverse is not just an idea but a reality.
Nike – one of the biggest and most famous brands in the world – filed several trademarks late last year, signaling its intention to create and sell virtual sneakers and clothes. It is the clothing company’s first step into the Metaverse. The trademark registrations clearly indicate Nike’s keen interest in capitalizing on the potential of the virtual space.

This is not the first time Nike has explored virtual reality. In May 2019, Nike partnered with “Fortnite,” where the characters wore Nike sneakers. The apparel company is also teaming up with Roblox to create a digital world named “Nikeland,” where users can dress up their avatars in Nike apparel. Moreover, Nike purchased the NFT studio RTFKT, which creates virtual sneakers and other collectibles. In December 2019, Nike secured a patent for “CryptoKicks,” for linking digital assets, such as NFTs, with physical products like sneakers.
Read more about Metaverse and NFT IP rights here. In the next section, we will discuss the best way to protect a brand in the Metaverse through trademarks.
How do Trademarks protect brands in the Metaverse?
Trademarks protect the identity of a company and the reputation of its brand(s), including in the Metaverse, by keeping imitators at bay. The trademark registration protects the owner and legally recognizes the company, thereby safeguarding the company’s interests. As a result, the registered trademark’s owner will have exclusive rights to use the trademark and access essential legal tools to prevent it from being used illegally by other entities. Some of the perks of using a trademark in the Metaverse are as follows:
- Makes it convenient and cost-effective for customers to find products
- Reduces marketing expenses
- Helps build brand identity
In Metaverse’s immersive reality, brand identification and differentiation will be crucial.
Let us discuss the advantages of registering trademarks in the light of the advent of the Metaverse.
Advantages of Registering Trademarks for Use in the Metaverse
Trademark registration is a must for any company that seeks to enjoy exclusive rights over a mark in a jurisdiction. The law not only protects the trademark in the real world but safeguards it against any infringement in the Metaverse as well. Therefore, just like trademark owners can initiate legal action against the sale of counterfeit products on online stores, they can litigate against infringement in virtual environments. However, it is critical to note that the trademark owner should register the mark for digital goods and services since a trademark for clothing does not extend to virtual clothes.
Moreover, legal protection available after trademark registration is not limited to the class of products and services of trademark registration. A trademark owner can also prevent the unauthorized use of the trademark for unrelated products and services in case the third party is taking undue advantage of or harming the distinctive character or reputation of the mark.
Now that you are familiar with the advantages of registering trademarks in the Metaverse, let us see the process of obtaining a trademark for use in the digital universe.
Obtaining a Metaverse Trademark
Mentioned below is the process to obtain a trademark for the Metaverse:
Step 1: Check whether or not the trademark is available
Check if your trademark is registrable in the United States. This entails a thorough search of the US trademark registry database to see if any identical or similar trademarks have already been registered.
Step 2: File your application
After ensuring no same or similar marks exist in the trademark database, and gathering all the essential information, file your application with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO).
Step 3: Trademark validity check
The Trademark Examiner examines the trademark on numerous grounds.
Step 4: Trademark Office decision and clearance
- If inappropriate information or errors are discovered, a notice is provided regarding the application. A reasonable timeframe is given to the applicant to rectify the data or reapply for application approval.
- In case of no objections, the examiner forwards the form to the Official Trademark Gazette.
Step 5: Opposition
After the trademark is published, other companies and individuals have 30 days to file an opposition to the trademark.
Step 6: Final registration process
If neither the opposition nor the Trademark Examiner raises any objections, the trademark registration application is eventually authorized and finalized. A ‘notice of allowance’ is also provided. Further, we delve into the methods of trademark protection in the Metaverse.
Protecting a Trademark in the Metaverse
1. To get a trademark registered under the USPTO, the trademark owner must run a trademark search to ensure that no identical trademark exists. Early filing of applications, i.e., even before the official commencement of business, is recommended by most authorities to avoid unprotected use of the mark and legal battles in the future over its ownership.
Trademark registration with the USPTO or other trademark offices is highly recommended among brand owners. It grants exclusive rights over the product to the owner. It allows the trademark owner to enforce rights against the unauthorized use of marks in real and virtual worlds. Another crucial step in this process is to keep track of the application status until the trademarks are officially used on products in the Metaverse.
2. Trademark owners should refrain from using generic and descriptive trademarks as they offer little protection, and rival brand owners can use them by substituting synonymous words. Distinct trademarks are not only convenient to register but also comparatively easier to defend in a court of law.
3. Extensive licensing of trademarks can help brand owners to curb open access to their products in the Metaverse. By way of licensing, the brand owners prevent third-party infringement while earning royalty payments.
4. Trademark owners should keep a tab on all the IPs owned. The owners can avail, by way of subscription, trademark monitoring services to identify any infringement activities or establish a system within the place of business, comprising experts, to keep a close watch on market trends and thereby impede such violations. This way, the owner can take appropriate action to limit such breaches before it is too late.
5. Building the brand in the Metaverse is yet another way of protecting one’s trademarks. Consumers’ widespread acknowledgment of the brand is in itself protection as offenders usually hesitate to imitate famous brand logos, fearing severe legal repercussions.
In the following section, we will explore IP issues that brands need to consider with the advent of the Metaverse.
Trademark-related Issues in the Metaverse
While mixed and augmented realities have given brand owners access to develop a new industry and customer base, it has also caused problems for trademark owners and users, particularly in the gaming industry. For example, a common problem with the intersection of the virtual and real worlds has been the use of real-world, third-party trademarks in video games that simulate the real world.
An early example of the possible hazards of using real-world trademarks in the virtual world is ESS Entertainment 2000, Inc vs Rock Star Videos, Inc (9th Cir. 2008). The issue, in this case, was whether a virtual representation of a real-life strip club in the famous game ‘Grand Theft Auto: San Andreas’ infringed on the real-life strip club’s logo and trademark rights. The court ultimately decided that the strip club’s depiction in the video game did not infringe on the strip club owner’s trademarks and trade dress rights because the video game was a work of art protected under the First Amendment, and consumers were unlikely to be misled into believing that the strip club created the sophisticated video game.
Many concerns surrounding the use of third-party trademarks in virtual worlds have developed due to the proliferation of user-generated content in recent decades and online “virtual world” games such as Pokemon Go, The Sims, and Second Life. Second Life, for example, a major multiplayer role-playing game with an online economy, allows users to construct their own virtual worlds, develop and market the intellectual property, and even sell their own branded products for profit. Second Life users can even create an online business presence to sell their products in the real world. These advantages, however, come with the danger of unauthorized use of third-party trademarks and potential brand dilution.
For example, avatars can sell and buy virtual items bearing third-party trademarks. Therefore, trademark owners should be aware of the dangers of using their brands in these virtual worlds. While the law governing the use of trademarks in the digital space is still evolving, the following examples highlight some of the challenges that have arisen:
- Minsky vs. Linden Research, Inc: In this case, the plaintiff dubbed his art gallery “SLART” and opened it in the virtual reality game Second Life. The plaintiff obtained a registration for the mark SLART with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and later discovered that a user-created avatar in the popular game was using SLART GARDEN for its virtual art gallery. The court never reached a decision on the case’s merits since it was eventually settled.
- Leo Pellegrino vs. Epic Games, Inc: The plaintiff, in this case, a saxophonist whose dance moves went viral on the internet, sued the creator of the popular video game Fortnite, claiming that the game presented a virtual saxophone-playing avatar that copied his dancing moves. The court dismissed Pellegrino’s claim of a violation of his right to privacy based on the First Amendment. According to the court, Pellegrino’s trademark claim was also denied because the allegations were better suited to copyright law. The court permitted Pellegrino’s claim for fraudulent endorsement to proceed; however, Pellegrino dismissed his complaint after the court’s judgment.
- AM General vs. Activision Blizzard: In this case, AM General, the manufacturer of the Humvee truck, filed a trademark infringement lawsuit against Activision Blizzard for featuring the truck in Activision’s Call of Duty video game. The court upheld Activision Blizzard’s summary judgment claim under the First Amendment, stating that “Defendant’s use of Humvees in Call of Duty games has artistic relevance” and that “featuring actual vehicles used by military operations around the world in video games about simulated modern warfare surely evokes a sense of realism and lifelikeness.” A common theme among such cases is that the risk of liability for using third-party trademarks is much greater when the trademarks are used for commercial benefit.
The next section highlights the best practices for trademark owners.
Best Practices for Trademark Owners
Brand owners may need to assert their trademarks in the virtual world as the Metaverse grows and evolves, blurring the boundaries between the real and virtual worlds. Brand owners should consider the following to safeguard their valuable trademarks:
- Register the trademark: Brand owners are strongly urged to register their trademarks with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and foreign equivalents. In the United States, it provides a rebuttable presumption that the owner has the exclusive right to use its trademark in connection with its goods or services. It puts the owner in a far better position to enforce action against any unlawful use of its mark in the virtual or real world.
- Consider signing up for a trademark monitoring service: A trademark owner cannot keep track of every infringing usage in the market, especially if the trademark portfolio is vast. As a result, trademark monitoring services enable trademark owners to watch relevant markets and internet content for potential infringement. Owners can be notified of infringing conduct sooner rather than later by engaging with a monitoring service and take prompt action if any issues arise. They can also consider appointing a third party to analyze these reports as they come.
- Notify the platform right away if there is any infringing activity: Brand owners should report to the platform every instance of infringement by a third-party platform user. Many of these companies do not want to be held liable for any contributory infringement, so they tend to put in place procedures to remove infringing content as soon as they become aware of it.
- Examine the nature of the use and any possible claims: Once you have become aware of possible infringing activity, the next step is to consider the nature of the infringing usage and how it affects the entire brand and the market for the goods/services connected with the brand. Not all trademark usage in the Metaverse is actionable. Outside counsel can help with this examination and determine what difficulties may exist in the trademark’s enforcement. It is also worth noting that in the United States, nationally recognized or “famous” brands have a better chance of enforcement against unauthorized use because they can sue under the Federal Trademark Dilution Act if the use of their trademarks “tarnishes” or “blurs” the trademark. Regardless of whether or not consumers are confused about the origin of the goods, the act applies.
- Establish a presence in the Metaverse: Finally, brand owners should consider building their Metaverse presence. Apart from the advantages of using the Metaverse as an alternative means of reaching consumers and developing brand recognition in a thriving and growing industry, it also allows for activity monitoring and may even assist in thwarting trademark infringement by criminal actors.
Why Choose Sagacious IP for Trademark Search?
Since trademarks are essential in the real world as well as the Metaverse, it is necessary to conduct a thorough search before registering one to avoid infringement. The following are some of the reasons why Sagacious IP is the ideal trademark search partner for you:
- A dedicated team of over 20 trademark experts with several years of experience.
- Ability to search for existing trademarks that are exact, near-exact, or similar sounding in the same classifications and goods & services.
- Ability to conduct global, cluster-based, and localized trademark searches.
- Proven track record of delivering high-quality services to clients.
- State-of-the-art tools to provide accurate and reliable search results.
- Customised delivery schedules.
- Solutions that are both affordable and effective.
Our trademark experts specialize in providing customized search services to our clients. To create a complete report on these searches, we cover all potential combinations, distinct variations, and phonetically related marks in our trademark search.
Conclusion
The aspects of the Metaverse continue to evolve at a rapid pace. It is challenging to develop a corporate strategy in such a volatile environment, characterized by rapid growth and new entrant innovation. The risks and costs of engaging early and consistently in the development of the appropriate intellectual property, developing hypotheses about future business models, and identifying ecosystem partners and collaborators are, on the other hand, relatively low. The asymmetrical risk of being left behind justifies the modest initial investment required to get started and explore this new digital landscape. Brand owners who want to succeed in the Metaverse should think about intellectual property ownership and the risks and benefits that come with it.
Sagacious IP’s trademark searches help companies find precise and comparable trademarks in the same sectors or for the same goods and services. Our trademark search team is committed to delivering the most comprehensive trademark search reports in a timely and cost-effective manner. Click here to learn more about the Trademark Search service. You can also look at the numerous other services we offer on our website.
– Amruta Shivshankar Bondre, Priyanka Nimje (Trademark) and the Editorial Team




