Effective Strategies for Patent Cooperation Treaty National Filings
The Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) provides a streamlined and efficient process for patent applicants seeking protection in multiple countries. Once an international PCT application (or a WIPO or WO application) is filed, it undergoes a specific sequence of events culminating in the national phase filing. This critical phase involves transitioning the international application into individual national or regional patent offices for examination and granting of patents.
- Generally, the transition from the international phase to the national phase typically occurs 30 months from the priority date (the filing date of the earliest application from which priority is claimed).
- Entering the national phase of a PCT application involves critical steps and careful preparation to ensure successful patent protection in designated countries.
Following the submission of an international patent application through the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), inventors are faced with a crucial decision: which patents should be pursued for national filing? This decision carries significant implications for the future protection and commercialization of their inventions. With limited resources and diverse legal landscapes across jurisdictions, prioritizing patents for national filing requires a strategic approach.
In this article, we delve into the best practices for prioritizing patents for national filing after the PCT stage. Additionally, we explore the factors that influence decision-making and the methodologies employed by us, which help in safeguarding innovations in an increasingly competitive global market.
Table of Contents
Mega and Wider National Filings
The PCT applications shortlisted for the national phase are bifurcated into two categories – Mega Filings and Wider Filings. The Mega filings include filing applications in the majority of jurisdictions, while in wider filings, the selected application is filed in prominent jurisdictions like the US, EP, CN, JP, etc.
These typically include major economic powers and key markets such as the United States (US), the European Patent Office (EP), China (CN), and Japan (JP). The Wider Filing strategy allows companies to balance the need for protection in crucial markets with the desire to manage costs effectively.
Therefore, this classification serves as a strategic tool for applicants to prioritize their patent protection efforts and allocate resources effectively based on the perceived importance and potential of each invention.
Need For Strategies for Shortlisting PCT Applications
The process of shortlisting Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) applications for national phase entry is a crucial step in any international patent strategy. This strategic approach offers numerous benefits that can significantly impact the success and efficiency of an inventor’s or company’s intellectual property management. Let’s explore the key reasons why developing strategies for shortlisting PCT applications is essential.
Cost Efficiency
One of the primary drivers for strategically shortlisting Patent Cooperation Treaty applications is cost efficiency. Specifically, by carefully selecting patents for national filings, inventors can prioritize jurisdictions where protection is most crucial. This targeted approach optimizes resource allocation, reducing unnecessary expenses associated with filing in every PCT member country. It allows for more judicious use of often limited patent budgets, ensuring that resources are invested where they will yield the greatest return.
Tailored Protection
Not all inventions have equal commercial potential in every market. Therefore, shortlisting patents for national filings enables inventors to tailor their protection strategy to target countries where their inventions are likely to have the greatest market demand or face the highest risk of infringement. This customized approach ensures that patent protection aligns closely with business objectives and market realities.
Strategic Expansion
By shortlisting patents for specific national filings, inventors can strategically expand their intellectual property portfolio in key markets. This targeted expansion enhances their competitive position and market presence while minimizing the risk of diluting resources in less relevant jurisdictions. It allows for a focused approach to building a strong patent portfolio that supports overall business strategy.
Timely Action
Filing national patents post-PCT submission ensures timely initiation of the examination process in selected countries. This can accelerate the grant of patent protection, providing early certainty regarding the enforceability of intellectual property rights. Timely action is particularly crucial in fast-moving industries where technology evolves rapidly.
Preservation of Options
Selecting patents for national filings preserves flexibility for future licensing, enforcement, or commercialization activities. It allows inventors to retain control over their inventions while exploring potential partnerships, collaborations, or investment opportunities on a country-specific basis. This flexibility can be invaluable as business strategies evolve and new opportunities emerge.
Risk Mitigation
By focusing on key jurisdictions through shortlisting, inventors can reduce the risk of potential conflicts or oppositions that may arise during the patent prosecution process. Allocate resources to address challenges or strengthen patents in priority markets, safeguarding against potential threats to intellectual property rights.
Market Access
National filings in strategic jurisdictions facilitate access to local markets. As a result, this enables inventors to capitalize on commercial opportunities, negotiate licensing agreements, or pursue manufacturing and distribution arrangements tailored to specific regions. It’s an essential step in translating intellectual property into tangible market presence and revenue streams.
Compliance Requirements
Different countries have varying legal and procedural requirements for patent applications. Therefore, shortlisting patents for national filings allows inventors to ensure compliance with jurisdiction-specific formalities and deadlines. This minimizes the risk of procedural errors or omissions that could jeopardize patent rights, ensuring a smoother path to patent grants in chosen jurisdictions.
Enhanced Portfolio Management
A strategic approach to shortlisting thus facilitates streamlined portfolio management. It allows inventors to focus resources on maintaining and enforcing patents that align with their strategic objectives and business priorities. This leads to a more manageable and impactful patent portfolio.
Strategic Flexibility
The dynamic nature of the market and technological landscape often necessitates adjustments to patent protection strategies over time. Therefore, shortlisting patents provides inventors with the flexibility to adapt their filing strategy in response to evolving business priorities, market conditions, or changes in the competitive landscape. This adaptability is crucial in maintaining a relevant and effective patent portfolio.
Hence, developing strategies for shortlisting Patent Cooperation Treaty applications is not just a matter of cost-saving; it’s a comprehensive approach to maximizing the value and impact of an international patent portfolio. By carefully considering these factors, inventors and companies can ensure that their patent strategy aligns closely with their business objectives, market realities, and resource constraints.
Methodology
The process of strategizing Patent Cooperation Treaty national filings involves a systematic approach to evaluate the potential and patentability of inventions. Specifically, this methodology consists of three crucial steps, each contributing to a comprehensive assessment that informs decision-making for national phase entries.
Step 1: Product Search Analysis
The first step in our methodology involves a detailed understanding of the invention and a thorough market analysis. This process includes:
- Invention Analysis: We begin with a comprehensive examination of the invention, scrutinizing its features, functionalities, and unique aspects. This deep dive allows us to fully grasp the technical nuances and potential applications of the invention.
- Market Research: Following the invention analysis, we conduct extensive research to identify existing products or technologies in the market. Our focus is on postdated products that may have similarities or overlaps with the invention in question.
- Overlap Assessment: We carefully evaluate the extent of overlap between the identified market products and the invention described in the WIPO application. This assessment helps gauge the uniqueness of the invention in the current market landscape.
- Market Applicability Evaluation: By synthesizing the information from the invention analysis, market research, and overlap assessment, we gain valuable insights into the market applicability of the WIPO application. Therefore, this evaluation helps determine the potential commercial value and market positioning of the invention.
The product search analysis step is crucial as it provides a real-world context for the invention, helping to inform decisions about its patentability and potential for commercialization.
Step 2: WIPO Search Report Analysis
The second step focuses on a thorough examination of the search reports provided by WIPO examiners. Furthermore, this analysis is critical for understanding the patent landscape and potential challenges to patentability. The process includes:
- Examiner Report Review: We meticulously review the search reports prepared by WIPO examiners. These reports often reveal potential prior art that could impact the patentability of the invention.
- Prior Art Assessment: We analyze the cited prior art references to understand their relevance to the invention, specifically evaluating how they might affect the novelty and inventive step of the application.
- Correlation Analysis: We examine the correlation between the cited prior art references and the WIPO application, as provided by the examiner. This step is crucial for understanding how the examiner views the invention in light of existing technology.
- Decision Evaluation: Based on our analysis, we determine whether the decision rendered in the search report is positive or negative, and more importantly, whether it is justifiable. We pay particular attention to the quality of the cited prior art and the accuracy of the mapping provided by the examiner.
- Quality Check: We’ve observed that examiner mappings can sometimes be inaccurate or overly broad. To mitigate this, we carry out our evaluation to resolve any missed or misjudged prior art issues.
This step provides critical insights into the novelty, inventive step, and potential patentability issues of the invention, helping applicants make informed decisions about proceeding with national phase entries.
Step 3: Claim Amendments
The final step in our methodology involves suggesting strategic claim amendments based on the findings from Steps 1 and 2. Thus, this process includes:
- Amendment Strategy Development: We formulate a strategy for claim amendments that addresses the issues identified in the product search and WIPO search report analyses.
- Enhancing Patentability: We design amendments to improve the application’s patentability by distinguishing the invention from identified prior art and market products.
- Tailoring to National Requirements: We ensure amendments align with national requirements, securing claims’ success in targeted jurisdictions.
- Novelty Preservation: Throughout the amendment process, we maintain a strong focus on preserving and highlighting the novelty of the application.
- Claim Strengthening Techniques: Common amendment strategies include:
- Appending dependent claims (for which no prior art was cited) to independent claims
- Incorporating suitable specifications or embodiments from the PCT application that weren’t previously included in the independent claims
By following this systematic methodology, we ensure a comprehensive evaluation of each PCT application, enabling informed decision-making for national phase entries. This approach maximizes the potential for successful patent grants while optimizing resource allocation in the complex landscape of international patent protection.
Exemplary Study
To illustrate the practical application of our methodology for strategizing Patent Cooperation Treaty national filings, let’s consider a case study involving a PCT application related to High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters. This example demonstrates how to leverage competitor analysis, market research, and IP landscape assessment to make informed decisions about jurisdictions for national phase entries.
Scenario: A PCT application for an innovative HEPA filter technology has been shortlisted for national phase entry. The task at hand is to determine the most strategic jurisdictions for filing.
Competitor Analysis
Using relevant Cooperative Patent Classification (CPC) codes and keywords for HEPA filters in patent databases, we identified the key players in the air filter space.
Here are the key findings:
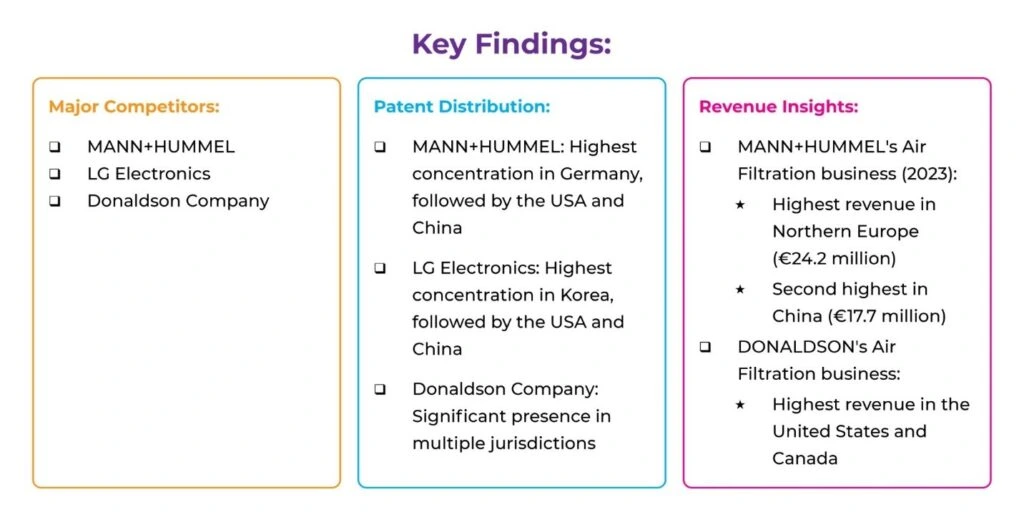
Initial Conclusion: Based on the competitor analysis, the USA, Europe, and China emerge as potential key jurisdictions for filing the PCT application related to HEPA filters.
Market & IP Research
In-depth market research and intellectual property (IP) analysis are crucial for developing an effective strategy for PCT national filings. Moreover, our study of the global HEPA filter market reveals regional variations in market dynamics and patent landscapes, presenting unique opportunities and challenges for patent applicants.
- North America plays a significant role in the HEPA filter market, with projections showing it will account for over 20% of global production. This is largely due to the region’s industrial landscape, which houses numerous manufacturing facilities that contribute significantly to pollution. As a result, there is a growing demand for efficient air filtration solutions in both residential and commercial spaces.
- In Europe, the HEPA filter market has experienced steady growth, supported by major investments in advanced facilities and technologies. A notable example is the establishment of the largest cleanroom facility in the Netherlands by the American Air Filter Company (AAF), which enhances manufacturing efficiency while reducing air contamination. Patent applicants should focus on European countries like the Netherlands, which offer cutting-edge manufacturing capabilities for national phase entries.
- The Asia Pacific region, particularly China and India, presents some of the most dynamic opportunities in the global HEPA filter market. Demand for air filtration technologies is rising rapidly due to increasing awareness of air quality issues. As a result, this region is expected to achieve the highest production growth rate in the coming years, making it crucial for a comprehensive patent strategy.
Additionally, a quick patent search reveals that the US and China lead in HEPA filter patents, suggesting a competitive market. However, India stands out with only 2.5% of total HEPA filter patents, indicating a less competitive IP environment. This offers a unique opportunity for companies to establish a strong patent position in India, where demand for air filters is growing rapidly.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, strategizing Patent Cooperation Treaty national filings is a critical component of maximizing the value of a patent portfolio while navigating the complexities of international patent protection. Based on the analysis of findings, applications that show a strong overlap with market products are recommended for extensive national filings.
In cases where direct market overlap is less apparent, but the application demonstrates potential through research trends or addresses similar challenges as existing products, broader national filings are encouraged. Entering the national phase of a Patent Cooperation Treaty application is a critical step in securing patent protection across multiple countries.
By thoroughly understanding specific requirements and seeking expert guidance, applicants can successfully navigate this phase and obtain valuable patent rights. Additionally, this strategic approach ensures targeted recommendations for national filings, helping clients build a stronger patent portfolio and competitive market presence.
– Amit Kumar, Pallavi Sinha (ICT Licensing)
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




