5 Patent Proofreading Steps For Legal Counsels To Avoid Patent Rejection
As an inventor or an IP professional, we know that patents are crucial for protecting inventions. However, to obtain a patent, an applicant needs to carefully prepare and then file an application with the concerned patent office. It is important to be cautious while drafting an application because even minute errors can impact the application and eventually lead to an office action or patent rejection. Proofreading is therefore the most important process that helps you save time and cost, mitigates risk of rejection as well as ensures patent enforceability.
Table of Contents
What is Patent Proofreading?
Patent proofreading is a process which helps in identifying and rectifying mistakes to ensure accurate and error-free patents. This process should be considered a crucial step before and even after the grant of a patent, primarily because patents riddled with errors not only impact enforceability but also waste time and cost invested in drafting them.
Types of Patent Proofreading
Now that you are aware of the concept of proofreading, let us discuss the various options that are readily available.
Depending on the requirement, proofreading can be performed for:
- Full patent – This involves proofreading all the components of a patent i.e. front/face page, abstract, specification, drawings, and claims.
- Partial patent – In this, only particular sections of a patent are proofread. This essentially involves face page and claims proofreading.
Based on specific elements of a patent, proofreading can be sub-categorized into the following three types:
- Face Page proofreading: This involves a complete review of the face page of a granted patent to identify errors. Notably, the face page is reviewed with relevant documents in Image File Wrapper and further checked to ensure that all amendments in the page have been implemented correctly.
- Drawings & Specifications proofreading: This sub-type checks drawings or designs to ensure that all drawing/design reference numbers have been accurately defined in the specification.
- Claims proofreading: This is done to make sure that all claims have been verified and respective claim amendments have been incorporated. Further, it highlights all antecedent errors as well as dependency errors.
Stages for Performing Proofreading
Whether it is the USPTO or the applicant that has made errors, the responsibility of correcting these errors lies on the applicant. Errors in the patent application may appear on the face page, in the claims section or in the complete specification including designs/drawings. Proofreading should therefore be performed at any of the following stages:
- Before filing the application
- Once the patent application is published
- Notice of allowance stage
- Once the patent is issued
- When PCT application is published – U.S. as the receiving office
Steps to Follow for an Error-Free Patent Application
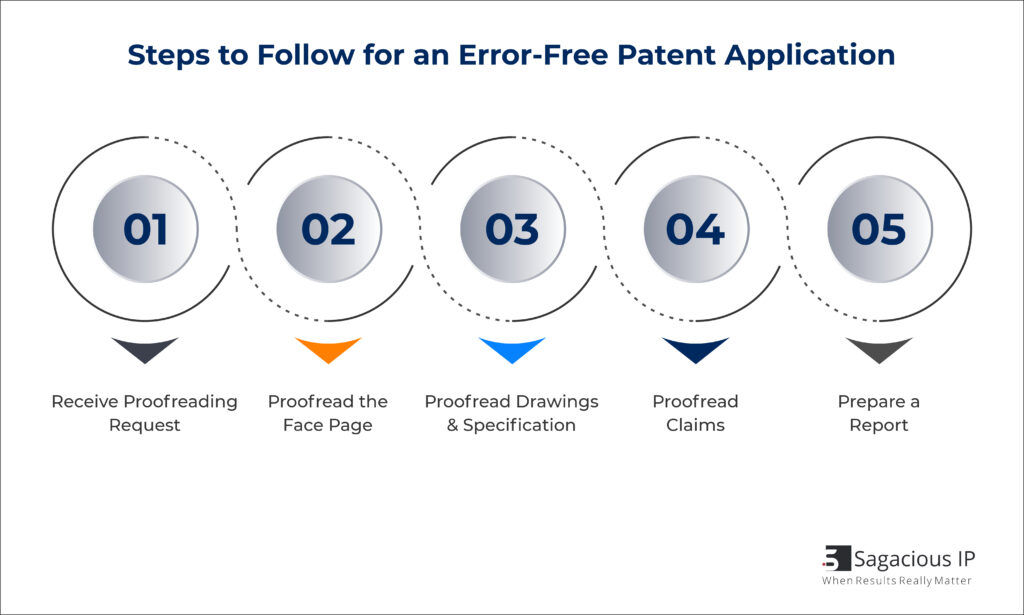
In this section, we will discuss the method of proofreading patent applications.
- Stage I: Receiving Proofreading Request
After receiving and acknowledging a proofreading request, the designated proofreader needs to download the granted patent as well as Image File Wrapper (IFW) documents.
- Stage II – Proofreading the Face Page
At this stage, a proofreader compares the face page of the granted patent line by line with IFW documents. Further, he/she cross checks if changes made to the face page have been implemented.
- Stage III – Proofreading Drawings & Specification
Drawings and the entire specification are reviewed to ensure that all drawing reference numerals have been clearly defined in the specification.
- Stage IV – Proofreading Claims
All claim amendments are assessed to ensure that changes have been incorporated. Furthermore, antecedent errors along with any dependency errors are highlighted.
- Stage V – Preparing a Report
After thoroughly reviewing the patent and IFW documents, a proofing error report which highlights the errors is prepared. Based on specific instructions, a Certificate of Correction (CoC) is drafted. Finally, a “Marked Issued Patent Report” which highlights errors in an issued patent is prepared.
Final Thoughts
Since a patent is crucial for protecting an invention, one cannot afford to have errors in these legal documents. Proofreading is an imperative process which can be conducted either pre-grant or post-grant of a patent to correct error-riddled documents. It allows the applicant to correct both significant and insignificant errors which affect patent enforceability. Sagacious IP’s Patent Proofreading service helps you identify errors in an issued patent by cross examination of communication documents stored in the IFW document of USPTO Public. Click here to know more about the service and click here to watch the webinar on the subject.
– Prateek Mohunta (COO), Sameer Kumar (IPMS) and the Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




