Accelerating Global Patent Protection: Role of Patent Prosecution Highway (PPH) & AI
In today’s globalized economy, protecting intellectual property across multiple jurisdictions is crucial for many businesses and inventors. However, the process of obtaining patents in different countries can be time-consuming, complex, and expensive. The Patent Prosecution Highway (PPH) has emerged as an innovative solution to address these challenges, offering a streamlined approach to accelerate patent examination in participating intellectual property offices worldwide.
In this article, we will discuss how the Patent Prosecution Highway (PPH) streamlines global patent protection, accelerates examination processes across multiple jurisdictions, and reduces costs for businesses and inventors.
Table of Contents
What is the Patent Prosecution Highway?
The Patent Prosecution Highway is a set of agreements between patent offices that allows applicants to request fast-tracked examination of a patent application in one jurisdiction if a corresponding application has been deemed to contain allowable claims in another participating jurisdiction. The primary goal of PPH is to speed up the patent prosecution process, reduce workload for patent offices, and provide a more efficient path to global patent protection.
How does PPH work?
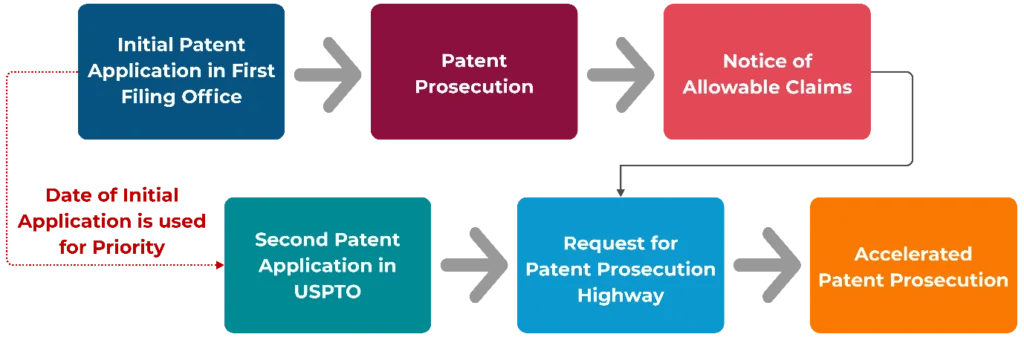
Figure 1: Process followed in PPH
The basic process of PPH involves three main steps:
- Examination Report: An applicant receives an examination report from a first patent office (Office of Earlier Examination or OEE) indicating that at least one claim in their application is allowable.
- PPH Request: The applicant files a request for accelerated examination under the PPH program with a second patent office (Office of Later Examination or OLE) where they have a corresponding application pending.
- Fast-Track Examination: If the PPH request is granted, the second office fast-tracks the examination of the application, leading to quicker prosecution and a higher likelihood of allowance.
Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible for the Patent Prosecution Highway, an application must meet several criteria:
- The OLE application must have the same earliest priority date as the OEE application containing the allowable claims.
- The OEE must have deemed at least one claim in the OEE application allowable.
- The claims in the OLE application must sufficiently correspond to the allowable claims in the OEE application.
- Substantive examination of the OLE application must not have begun at the time of the PPH request.
Types of PPH Programs
There are two main types of PPH programs:
Global PPH
This program includes a broad array of participating offices worldwide. It allows applicants to use the examination results from any participating office as the basis for a PPH request in another participating office.
Participating Offices: KIPO (Korea), JPO (Japan), USPTO (USA), CIPO (Canada), PRH (Finland), ROSPATENT (Russia), UKIPO (UK), NIPO (Norway), NPI (Nordic), DKPTO (Denmark), PRV (Sweden), INPI (Portugal), ISIPO (Iceland), IP Australia (Australia), HIPO (Hungary), IPOS (Singapore), APO (Austria), SPTO (Spain), ILPO (Israel), DPMA (Germany), EPA (Estonia), PPO (Poland), SIC (Colombia), IPONZ (New Zealand), VPI (Visegrad), INDECOPI (Peru), INAPI (Chile)
Example: The USPTO participates in both the Global PPH and the IP5 PPH pilot programs, allowing applicants to file a PPH request based on the work product of any office participating in either program. Since both programs have equivalent requirements, USPTO applicants do not need to specify which program they are using.
IP5 PPH
The IP5 PPH program is specifically between the five largest intellectual property offices in the world: the USPTO (United States), JPO (Japan), KIPO (Korea), EPO (Europe), and CNIPA (China). This program allows for PPH requests between these major offices.
While both programs offer similar benefits, the main difference lies in the participating offices. Some offices, like the USPTO, participate in both programs, allowing applicants more flexibility in their PPH strategies.
Benefits of Using the Patent Prosecution Highway
Utilizing the PPH offers several significant benefits:
- Faster Patent Grants: By leveraging positive results from one office, applicants can significantly reduce the time to grant in other jurisdictions. This allows for quicker building of global patent portfolios.
- Higher Grant Rates: Statistics show that applications examined under the PPH tend to have higher grant rates compared to regular applications, potentially due to the pre-screening effect of having allowable claims in another jurisdiction.
- Cost Reduction: With fewer office actions typically issued for PPH applications, overall prosecution costs can be reduced, despite the initial costs of preparing PPH requests.
- Improved Examination Quality: The sharing of search and examination results between offices can lead to more thorough and consistent examination across jurisdictions.
Documents Required for PPH Process
When filing a PPH request, applicants typically need to submit the following documents for examination in the second office:
- Copies and translations of the claims deemed patentable in the OEE
- Copies and translations of all relevant office actions issued by the OEE
- Copies of references cited by the OEE examiner
- A claims correspondence table mapping the OEE claims to the OLE claims
Timeframe for PPH Request
The process for filing a PPH request varies slightly between offices but generally involves submitting the required documents along with a formal request for participation in the PPH program. Once the PPH request is filed, the PPH request is generally decided within 4 months from the filing of the PPH request.
Examination Timeline: Once a PPH request is granted, the examiner will generally examine the application in the second patent office within 2 to 3 months from the grant of the PPH request provided the application has completed all its pre-exam processing and is ready for examination.
PPH Requests: Statistical Analysis
Global Trends
While PPH offers clear benefits, its usage is not as widespread as one might expect. However, the trend shows a gradual increase in PPH requests globally.
Leading Countries in PPH Usage
Data reveals that some countries, particularly the US, China, Japan, Korea, and Canada, are more active in PPH usage. This is likely due to these countries being early adopters of the PPH system and home to many large tech companies.
USPTO PPH Request Data
To illustrate PPH usage patterns, we can examine data from the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO):
Number of PPH requests with USPTO as the Office of Earlier Examination (OEE)
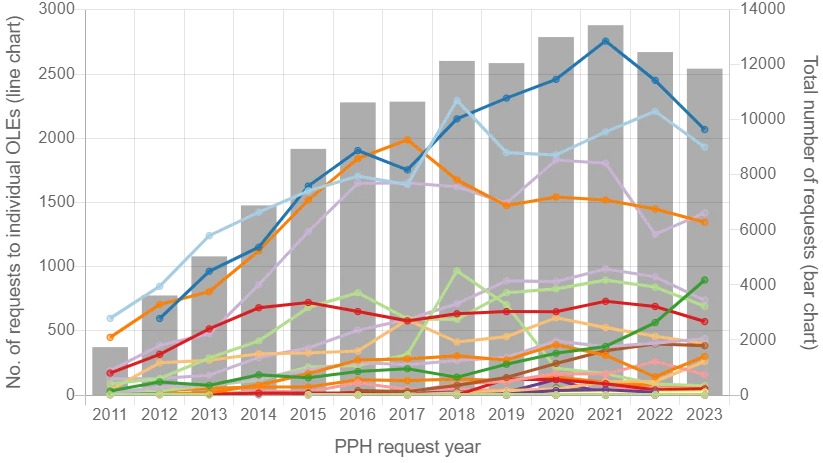
Figure 2: Number of PPH requests with USPTO as OEE
Number of PPH requests with USPTO as the Office of Later Examination (OLE)
This further illustrates the role of the USPTO in the PPH process.
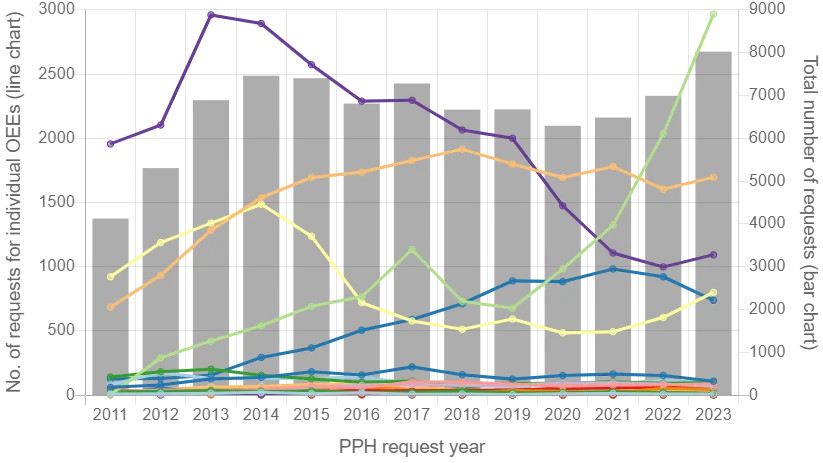
Figure 3: Number of PPH requests with USPTO as OLE
The data highlights the trends in PPH requests involving the USPTO, both as the office of earlier examination and later examination.
PPH Requests by Office of First Filing and Second Filing
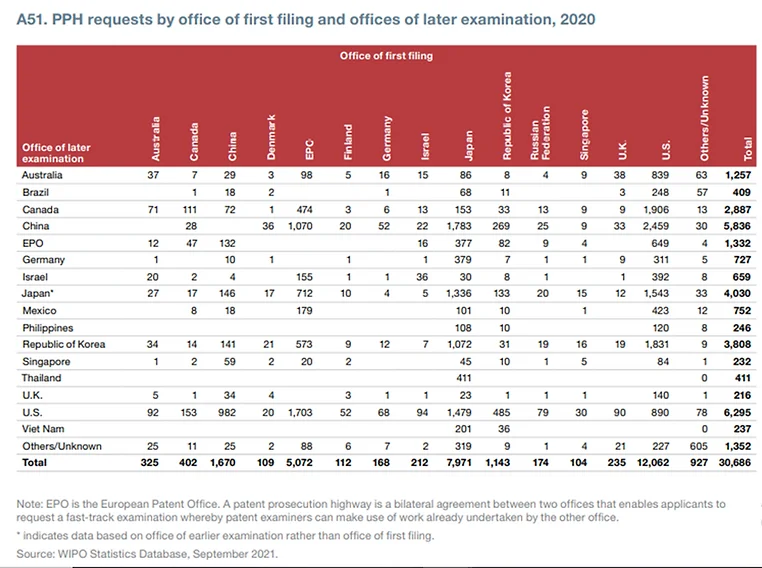
Figure 4: Number of PPH requests for Office of First Filing and Second Filing
The data depicts the PPH requests by the office of first filing and offices of later examination. Despite the many advantages, statistics show that PPH is not being used as widely as it should. The total number of filings amounts to 30,686. This is mainly due to the following reasons:
- Limited Claim Flexibility: The PPH restricts the ability to file broader or narrower claims in different jurisdictions.
- Lengthy and Costly Process: The prosecution process can be time-consuming and expensive, involving multiple exchanges between the examiner and the patent attorney.
- Tedious Formalities: Handling numerous formalities can be cumbersome and problematic.
- Inconsistent Regulations: Varying regulations and procedures across countries can lead to inconsistencies.
Upon analysis, it is evident that the US, China, Japan, Korea, and Canada are more active in PPH usage. This can be attributed to their early adoption of the PPH system and their status as hubs for large tech companies capable of managing PPH procedures.
PPH Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, the PPH faces several challenges and limitations:
- Claim Flexibility Issues: the requirement for claims to correspond between applications can limit an applicant’s ability to pursue broader or narrower claim scope in different jurisdictions.
- Cost Considerations: while PPH can reduce overall costs, the initial costs of preparing and filing PPH requests, including translations and formal documents, can be substantial.
- Procedural Complexities: the varying regulations and procedures between different patent offices can create inconsistencies and make the process challenging to navigate.
- Strategic Timing Concerns: the need to have allowable claims in one jurisdiction before filing a PPH request in another can sometimes conflict with strategic prosecution timing.
The Role of AI in Patent Prosecution and PPH
AI is revolutionizing patent prosecution and the PPH process by enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Here is some keyways AI can assist in patent prosecution:
- Drafting Assistance: AI can provide a ready-to-draft shell to a patent applicant, including fetching bibliographic details in office responses.
- Legal Analysis: AI can identify which section of US patent law an examiner is invoking to reject a claim and the corresponding section in the cited prior art.
- Predictive Analysis: AI can analyze historical patent data to predict the likelihood of a patent application being granted or rejected based on prior art and examiner behavior.
Areas for Automation
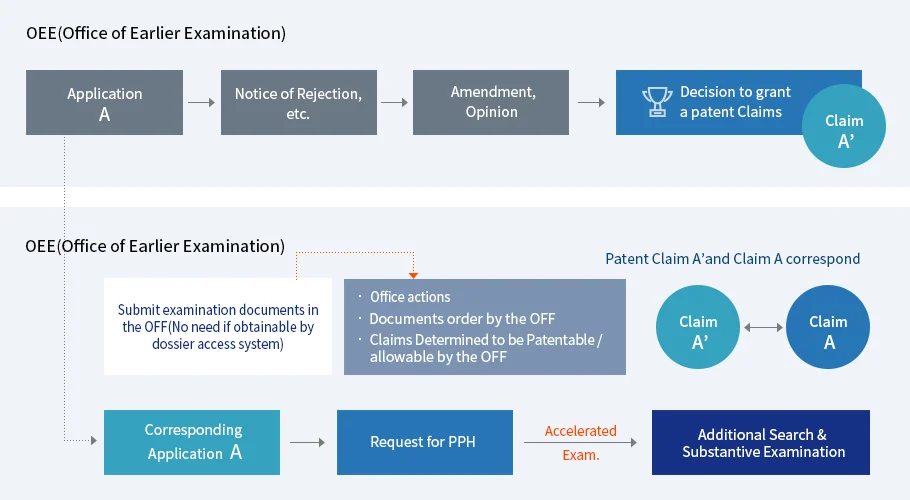
Figure 5: Automation Areas
- Data about the Patent Application: Accessing information about the patent application’s family from patent jurisdiction databases to find the corresponding application (similar invention).
- Data about the Corresponding Patent Application: Evaluating the allowability of claims by analyzing the file wrapper corresponding to the patent application.
- Choosing the Application with the Broadest Claims: Comparing various corresponding applications of the patent family with allowable claims to choose the application with the broadest claims for the PPH.
- Jurisdiction Data: Collecting information about jurisdictions and their grant rates where the accelerated examination is to be requested or PPH is to be filed, helping determine the grant rate of one’s PPH if filed in that respective jurisdiction. For example, determining the grant rate of a Japanese application in USPTO using PPH.
This includes analyzing the grant rate of an application (belonging to a particular jurisdiction) in another jurisdiction using PPH. For example, determining the grant rate of a Japanese application in USPTO using PPH.
Using AI for Document Submission
AI can streamline the preparation and submission of documents required for the PPH process:
- Automated Translation: AI-powered translation tools can be used to translate claims and office actions into the language of the Office of Later Examination (OLE).
- Automated Claims Correspondence Table: AI can be used to automatically generate a claims correspondence table, mapping the claims in the OEE application to the corresponding claims in the OLE application.
Future of PPH and Patent Prosecution
Evolving Landscape
As the global patent landscape continues to evolve, the PPH is likely to play an increasingly important role. However, its effectiveness will depend on continued cooperation between patent offices and ongoing efforts to streamline and harmonize processes.
Integration of AI and Automation
The integration of AI and automation technologies into PPH and broader patent prosecution processes holds great promise for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing the quality of patent examination. As these technologies mature, we can expect to see more sophisticated tools and systems supporting both applicants and patent offices in navigating the complex world of global patent protection.
Conclusion
The Patent Prosecution Highway represents a significant step towards more efficient and harmonized global patent prosecution. While it offers clear benefits in terms of faster grants and potential cost savings, applicants must carefully consider their global patent strategy when deciding whether to utilize the PPH system. As AI and automation technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see further improvements in the efficiency and effectiveness of PPH and patent prosecution processes, ultimately benefiting inventors, companies, and the broader innovation ecosystem. The future of patent prosecution will likely feature increased speed, efficiency, and global harmonization, with the PPH playing a crucial role in this evolution.
Sagacious IP can help navigate the complexities of the PPH system and leverage AI and automation technologies to optimize your global patent strategy. With expert guidance and cutting-edge tools, we ensure that your patent applications are handled efficiently and effectively, providing you with a competitive edge in the global market. To know more visit our Strategic Patent Prosecution Support service page.
– By Yoshita Gupta (ICT Drafting & Prosecution) and the Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




