Sequence Listing for Biotechnology Patents: A Beginner’s Guide
A Beginner’s Guide to Sequence Listing for Professionals Seeking Biotechnology Patents: Inventions in biotechnology involve gene mutation, gene sequencing, and regulating, expressing, or silencing of genes. Their patent specifications require a detailed description of the sequences. Therefore, when inventors file such a patent, all the DNA and protein sequences need to be entered into the patent specifications and are required to have a particular structure instead of the raw format. This is known as Sequence Listing, which is basically a process of taking the raw sequences and entering them in the required format as per the guidelines of the patent offices.
A gene consists of a chain of polynucleotides consisting of the nucleotides adenine (A), thymine (T)/uracil (U), cytosine(C) and guanine (G) that is code for amino acids. A protein consists of amino acids (i.e., 20 amino acids that occur naturally). A special one-letter code represents each amino acid. A sequence listing recognizes the gene or protein by means of a “SEQ ID NO.” (E.g. SEQ ID NO: 1) and provides the whole sequence.
Table of Contents
Who needs Sequence Listing For Biotechnology Patents?
Inventions that fall under biotechnology domain and revolve around mutation in genes, gene sequencing, gene regulations require sequence listing. Broadly, anyone who has sequences in their patent is obligated by the patent office to list the sequences in a proper format. Researchers, research scholars, scientists, law firms in biotech, or anyone working in biotechnology domain who wants to file a patent for their invention will need sequence listing.
Sequence Listing For Biotechnology Patents Process
When, an applicant has filed an application containing nucleotide and/or amino acid sequence, the description must contain a sequence listing. Such sequence must be prepared in accordance with “guidelines for the preparation of specification that contains amino acid/nucleotide sequences”.
At the time of application filling, a computer-readable form of sequence listing (i.e., electronic data) must be submitted. Submission of the electronic data is done by submitting a disc storing the data. Applicants can submit sequence listings for U.S. as well as international patent applications.
Un-branched sequences containing four or more amino acids or ten or more nucleotides can also be included. The basic definition omits branched sequences and sequences with less than four unique nucleotides/or amino acids.
Sequence listing lists nucleotide and/or amino acid sequence (biological sequences) in a specific format specified by WIPO Standard ST.25 (i.e. nucleotide and/or amino acid sequence listing) using standardized vocabulary (i.e. defined words for certain features).
There are mainly three methods for submitting biological sequence to a requesting office:
- Disc (containing an ASCII text computer-readable form on Disk/CD).
- Paperless Submission (submissions of CD, without paper)
- ASCII text (uploaded via Electronic Filing System
Mentioned below is an example of a Protein Sequence:
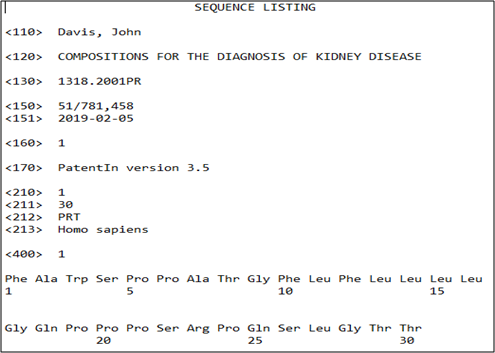
Here you can see how raw sequences look like in a proper Sequence listing format:
Protein Sequence provided by Client –
FAWSPPATGF LFLLLLGQPP PSRPQSLGTT
Output of Sequence listing (By Sagacious IP) –
Sequence Listing – Advantages
Sequence listing allows the applicant to create a single sequence list that is acceptable to all receiving Offices, Preliminary Examining Authorities and International Searching Authorities for international phase purposes, as well as to all designated and elected National Phase Offices.
Simpler presentation of the sequence helps candidates, examiners and public to access or search sequence data easily. It also increases the accuracy of amino acid and/or nucleotide sequences that make it easy to understand by the public.
Sequence listing also allows the exchange of sequence data in electronic form and the introduction of sequence data onto computerized databases.
Our Service
Sagacious IP is adept in ensuring that sequences are laid out in a proper format. We prepare documents in accordance with the WIPO standards for a smoother filing process. Let us look at a few case studies on our sequence listing service:
Case Study I
One of our clients – a US based law firm wanted to file an International Patent Application; wherein the patent application comprised nucleotide and protein sequences. Hence, to meet US (37 CFR §§1.821-1.825) and foreign (WIPO Standard ST.25) sequence listing requirements, the client was interested in preparing a computer readable “Sequence Listing” document required at the time of filing of the patent application containing biological sequences.
In the sequence listing project, Sagacious IP prepared an ASCII text computer-readable “Sequence Listing” document using PatentIn software 3.5 version. The DNA/RNA sequences also included modified nucleotides which were mentioned in the comment section for Artificial sequences/Unknown organism.
Case Study II
In another case, a client approached Sagacious IP to get corrections done in sequence listing for which objections have been received from the USPTO. The client was unaware of all the errors in the report. So, he wanted Sagacious IP to help him with identifying and consequently correcting all the errors in the report.
After understanding the client requirements, Sagacious IP prepared a corrected version for the sequence listing document which was aligned with US (37 CFR §§1.821-1.825) and acceptable by the USPTO.
Final Thoughts
For biotechnology related technologies, an applicant might need to file an application containing nucleotide and/or amino acid sequence and the description must contain a sequence listing. Such sequence must be prepared in accordance with “Guidelines for the preparation of specification that contains amino acid/ nucleotide sequences.” Sagacious IP is adept in creating the required sequence listing reports as per the set industry standards. Reach out to us for our expertise in sequence listing service.
-Pooja Chhikara (Life Sciences) and the Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




