AI in Patent Prosecution: The New Frontier in Filing a Patent and Improving Processes
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing patent prosecution and the process of filing a patent, transforming how applications are drafted, analyzed, and managed. One of the most impactful advantages of AI is its predictive capabilities, which analyze factors such as examiner behaviour and prosecution history to evaluate the likelihood of success for a patent application. This article explores AI’s role in patent prosecution and filing a patent, highlighting the key tools, benefits, challenges, and future prospects of AI in this essential field.
Table of Contents
AI-Driven Innovations in Patent Prosecution
AI-powered tools, such as Claim Master, are transforming the preparation of draft responses in patent prosecution. These tools leverage advanced macros and cutting-edge software to automate the generation of shell responses and identify errors in claims. By reducing human intervention, they help detect non-compliance issues, antecedent errors, incorrect numbering, and status identifiers, thereby enhancing the quality and consistency of patent applications.
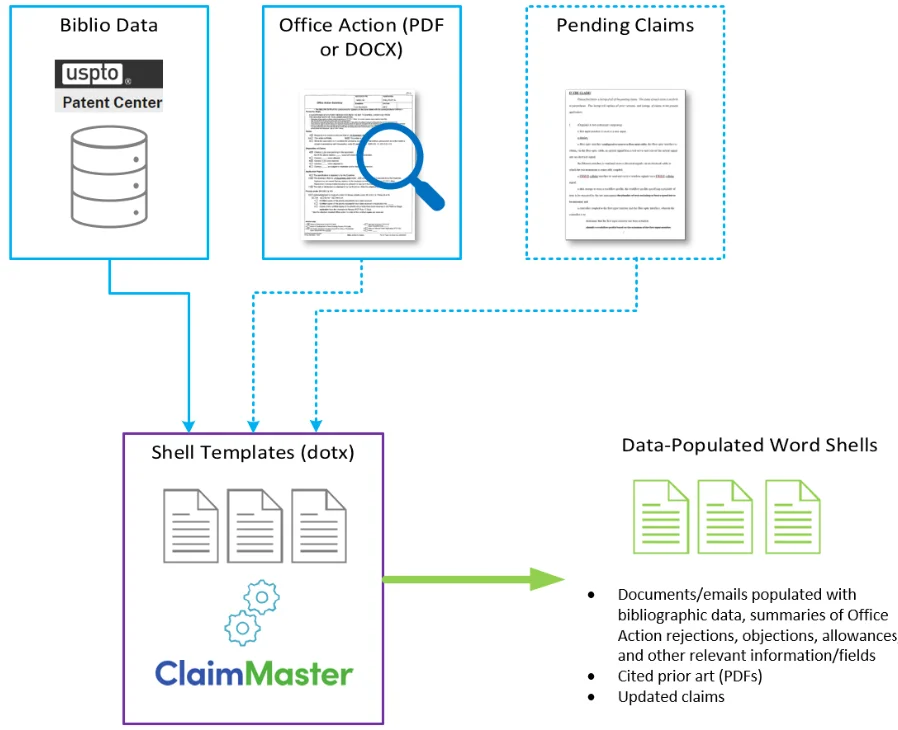
Pioneering AI Tools in Patent Prosecution
Several AI tools are making a substantial impact on patent prosecution. Notable examples include:
- Patent Bots: A powerful AI tool designed to draft patent applications, respond to Office actions, and assist with prior art searches. It also generates patent claims and provides analytics on examiner behaviour.
- LexisNexis PatentAdvisor: By providing insights into examiner behaviour, this tool helps patent practitioners make data-driven decisions about their prosecution strategies.
- Anaqua: Anaqua’s AI capabilities automate workflows in patent prosecution, such as docketing, tracking, and reporting, ensuring compliance with USPTO rules while managing deadlines effectively.
- ROSS Intelligence: Primarily known for its legal research capabilities, ROSS Intelligence leverages AI to identify relevant case law and references, assisting in the preparation of evidence for patentability or unpatentability.
Advantages of AI in Patent Prosecution
The implementation of AI in patent prosecution offers several advantages:
- Increased Efficiency: AI can automate routine tasks like docketing and tracking deadlines, allowing patent practitioners to focus on more complex tasks such as drafting applications and responding to Office actions. This reduces the risk of errors and improves overall efficiency.
- Cost Savings: By automating routine processes and improving efficiency, AI can significantly reduce the costs associated with patent prosecution, which is beneficial for those involved in filing a patent, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and individual inventors.
- Data-Driven Insights: AI can analyze large datasets to identify trends and patterns, enabling patent practitioners to tailor their strategies and improve the likelihood of success in filing a patent. For example, AI can highlight common reasons for rejection, allowing practitioners to address potential issues proactively.
Challenges of AI in Patent Prosecution
While AI is revolutionizing patent prosecution, several challenges must be addressed:
- Nuanced Understanding: AI may struggle with the complexities of patent law, such as interpreting ambiguous claims in the context of filing a patent. Human oversight is essential for handling intricate cases that require a deeper legal understanding.
- Legal and Ethical Concerns: Issues like the ownership of AI-generated content and the admissibility of AI-generated evidence raise legal and ethical questions. Clear guidelines are needed to navigate these concerns.
- Transparency and Explainability: AI systems need to provide transparent and explainable decisions to maintain trust. Users must be able to understand how AI-derived outcomes are determined, especially in legal contexts.
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can perpetuate biases present in their training data. Ensuring fairness involves using diverse datasets and regularly auditing AI tools to prevent discriminatory outcomes.
- Implementation Costs: While AI can reduce costs in the long run, the initial investment and ongoing maintenance can be expensive. Organizations must evaluate whether the benefits of AI outweigh these costs.
Survey Findings: How AI is Perceived in Patent Examination
As AI continues to transform various aspects of intellectual property (IP) prosecution, understanding the perspectives of those directly involved in the process is crucial. In our research, we found insightful survey data that highlights the experiences, concerns, and expectations of IP professionals regarding the use of AI in patent examination.
Key Findings from the Survey
In the survey diverse group of IP practitioners, covered a wide range of topics—from the current use of AI tools in IP prosecution to ethical considerations and future expectations. Here are some of the key findings:
- Familiarity with AI: A significant portion of respondents (43%) indicated that they are not currently using AI in their practice, reflecting a gap between AI’s potential and its current adoption. However, 64% expect minimal changes to their roles due to AI, suggesting a cautious optimism about AI’s impact.
- Perceived Benefits: When asked about the most significant benefits of AI in IP prosecution, the majority highlighted increased efficiency and improved accuracy, underscoring AI’s potential to streamline patent examination processes.
- Concerns About AI: Despite the optimism, there are concerns that cannot be overlooked. Bias and fairness emerged as the primary concern for 49% of respondents, followed by issues related to data privacy and lack of transparency.
- Current Use of AI Tools: Interestingly, 37% of respondents reported using AI-assisted search and classification tools, while 29% have adopted AI-powered patent drafting solutions. These numbers indicate that while AI adoption is on the rise, there is still significant room for growth.
- Future Outlook: Looking ahead, 55% of respondents believe that AI will become an essential tool for IP prosecution within the next five years, while a smaller group remains uncertain about its long-term impact.
The Potential for AI to Reduce Subjectivity in Patent Examination
The patent system plays a crucial role in promoting innovation and economic growth. However, persistent problems have long plagued the system, particularly the issue of subjectivity in patent examination. Patent examiners, being human, often exhibit biases and inconsistencies in their decision-making processes. This can lead to unfair outcomes, where some inventors receive patents while others do not, despite having similar inventions. The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has opened up new possibilities for reducing subjectivity in patent examination. By leveraging AI algorithms trained on extensive datasets of patent applications and outcomes, we can reduce human biases and provide more objective assessments. Here’s a closer look at how AI can enhance patent examination processes:
- Enhancing Prior Art Searches: One significant application of AI in patent examination is in the realm of prior art searches. Prior art search involves examining existing patents and other documents to determine if an invention is novel and non-obvious. Traditionally, this process is manual and time-consuming, often leading to incomplete searches and subjective decisions.
- Improving Patent Claim Evaluation: Patent claims define the scope of an invention and are essential for determining its patentability. AI can assist in evaluating these claims by identifying issues such as ambiguity or vagueness that might affect the clarity and enforceability of the patent.
- Streamlining the Patent Examination Process: AI can also enhance the overall efficiency of the patent examination process. For instance, AI algorithms can prioritize patent applications based on their likelihood of approval, thus allocating resources more effectively and addressing the backlog of applications.
AI Tool Deep Dive: A Closer Look at AI in Patent Prosecution
To fully understand the impact of AI in patent prosecution, it’s essential to explore the specific tools and technologies that are driving this transformation:
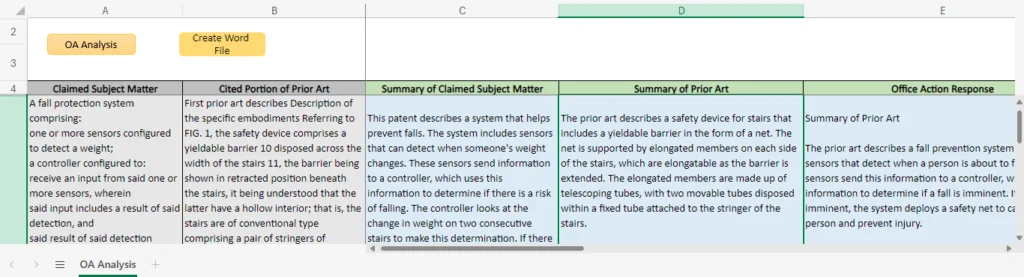
- Overview of the Tool: A comprehensive overview of a particular AI tool, including its objectives and the specific problems it aims to solve. For instance, a tool designed to automate prior art searches would focus on reducing the time and effort required to conduct thorough searches.
- Steps to Operate It: A step-by-step explanation of how to use the tool, including input parameters, processing steps, and expected outputs. Illustrations can offer a visual guide to the tool’s operation.
- Comparison with Manual Analysis and Response Drafts: A comparison of the time and effort required to perform the same tasks manually versus using AI tools. This section could highlight the advantages of AI, such as speed, accuracy, and consistency, while also acknowledging the areas where human expertise is still necessary.
- Technical Aspects of the AI Tools: A detailed discussion of the technical aspects of the AI tools, including the algorithms, models, and technologies used to develop and implement them. This section could also explore the challenges of developing AI tools, such as ensuring fairness, avoiding bias, and maintaining transparency.
- Future Scope of AI Tools: A forward-looking analysis of the potential future developments in AI tools for patent prosecution. This could include discussions of new features, improved algorithms, and the incorporation of insights from ongoing research in the field.
Case Study: IBM Watson in Patent Prosecution
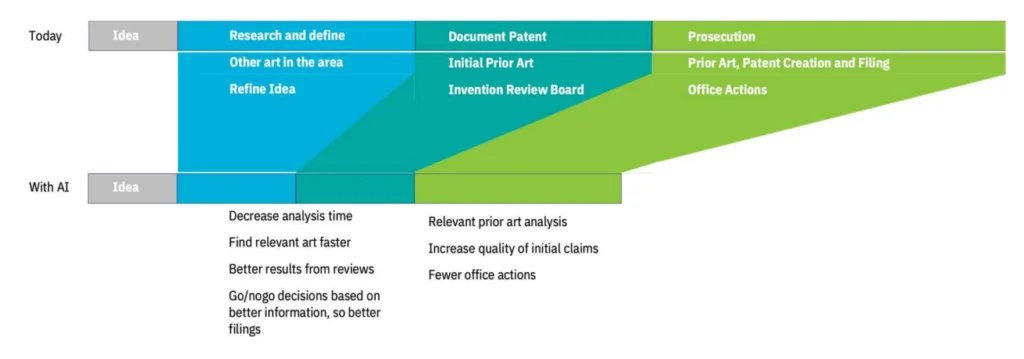
A notable example of AI in patent prosecution is IBM’s partnership with the USPTO in 2016, utilizing Watson for patent search and analysis. Watson’s advanced natural language processing and machine learning capabilities significantly reduced the time and cost associated with searching and analyzing patent applications while improving the accuracy of search results. This collaboration underscores AI’s potential to streamline patent prosecution processes and enhance overall outcomes.
Conclusion: The Future of AI in Patent Prosecution
AI holds the promise to significantly reduce subjectivity in patent examination by automating routine tasks, enhancing evaluation accuracy, and boosting overall efficiency. However, it is crucial to address challenges related to transparency, fairness, and cost to ensure AI’s benefits are fully realized across the patent system. Embracing AI can lead to a more objective, efficient, and equitable patent examination process, fostering increased innovation and growth.
As AI technology evolves, its role in filing a patent and patent prosecution will likely expand, making it an indispensable tool for patent practitioners worldwide. At Sagacious IP, we are dedicated to helping you leverage AI in your patent strategies. Our expert services can guide you through this technological shift, ensuring you remain competitive in the dynamic field of patent prosecution. Partner with us to optimize your patent processes and achieve greater success with AI-driven solutions. For more information about our patent prosecution services, visit our website.
– Hetain Chopra and Yoshita Gupta (ICT Drafting and Prosecution) and Rahul Raj (Content Creation & Strategy)
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




