Patent Drafting: Complete Patent Specification Elements
When it comes to filing a patent application, the goal is simple – to clearly explain the patent examiner what your invention is and how it can be used. Patent Specification, a document through which an inventor discloses the details of his invention, plays a crucial role in fulfilling the aforementioned aspect. Complete Patent specification significantly influence the possibility of a successful patent grant. The following article discusses various elements that are critical to the drafting of patent specifications.
Table of Contents
Patent Specification and Its Importance
A patent specification can be defined as a highly technical and legal document that discloses the invention to the public along with the best method of performing it. The language and the content of the patent specification has to be such that it enables the person ordinarily skilled in the art to practice the invention. Secondly, patent specifications should identify the subject matter over which the patent owner intends to claim exclusivity. The language of the document is generally full of technical and legal jargon as it contains scientific details of the invention.
Patent specifications must be drafted carefully from both legal and technical perspective. If the document does not sufficiently disclose the means to recreate the invention, the owner of the patent stands the risk of losing the grant. Similarly, if the scope of the invention is not defined accurately, it allows competitors to circumvent the patent and benefit from it. Therefore, one needs to draft technically sound patent specifications with due care.
Also Read: Critical Aspects of Patent Drafting in View of ‘Non-Obviousness Requirement’
Drafting Specifications Based on Type of Patent Application
- Provisional Patent Application: This type of patent application is filed by an applicant only to secure a patent filing date with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). It is filed when the inventor needs more time to perfect his/her invention. While filing a provisional application, the applicant is required to file only provisional patent specifications, which broadly, though not completely, disclose the inventive concept.
- Non-Provisional Patent Application: Also known as a regular patent application, a non-provisional patent application is filed within 12 months of filing a provisional application to secure patent rights for an invention. Regular patent application must include a complete specification of patent wherein the applicant discloses all details of an invention in a sufficiently clear and complete manner. In contrast to the provisional specifications, complete specification concludes at least one claim for which the protection is sought.
Elements of Complete Patent Specification
Now that the demarcation between the provisional and complete patent specification is clear, this section of the article explains the elements of the latter and how they should be drafted.
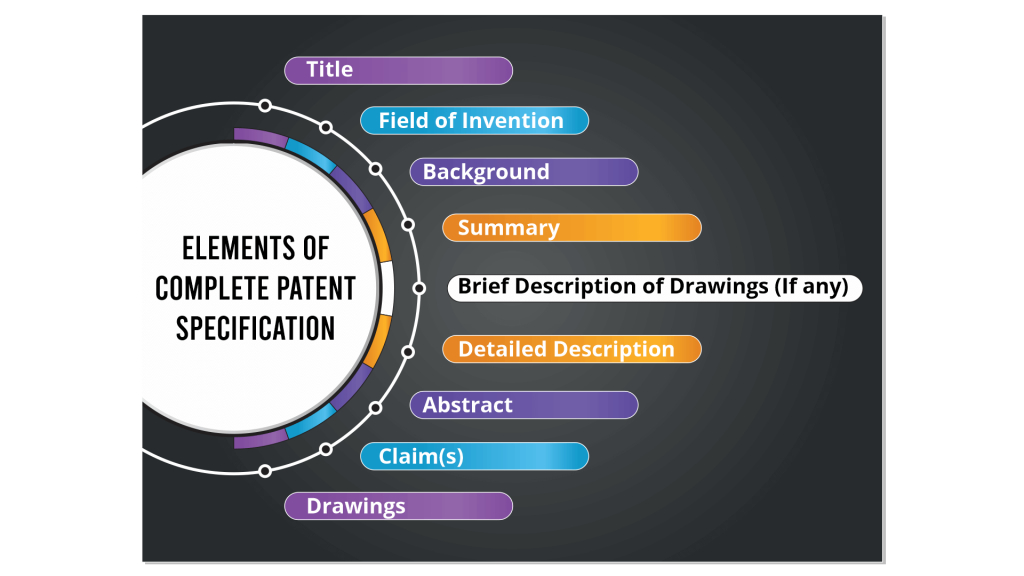
- Title: The first part of the complete patent specification should be the title of the invention. The applicant/patent agent must ensure that it fairly captures specific features of the invention. Secondly, the title shouldn’t include abbreviations, the word “patent”, etc. It must clearly spell the objective of the invention and should be between 10-15 words.
- Field of Invention: This is the section that highlights general and specific fields in which the subject matter of the invention falls. The field of invention helps the examiner to decide which search fields he/she can look into to find similar published technology, if any. This portion of the specification should ideally start with a general statement on invention to indicate the subject matter that the invention is related to.
- Background: This section briefly discusses prior arts and their drawbacks or disadvantages, if any. The main objective behind providing this information is to distinguish the invention at hand from the ones that are already being practiced in the targeted industry. The background section sets the stage for describing the invention in detail at a later stage.
- Summary: As the name suggests, summary gives a gist of the invention – its nature, objective, composition and operation. Most importantly, summary of the invention should come before the description of the claimed invention. Furthermore, the summary briefly mentions solutions to the problems talked about in the background section.
- Brief Description of Drawings, if any: Though not mandatory, patent applications often include drawings/flowcharts/figures to visually describe the invention, helping examiner to understand the innovation better. So this section presents a brief overview of the drawings. As per the guidelines of the USPTO, the figures should be clean black-and-white line drawings that accurately illustrate the invention.
- Detailed Description: This section focuses on providing sufficient details of the invention, including the structural details, how it is used, its objectives and advantages. Solutions achieved by the invention are covered in depth in this section. Most importantly, the detailed description should be provided in a manner that any person with ordinary skill in the art is able to practice the invention. Furthermore, this part may also include examples explaining the overall working of the invention in different environments and possible variations. Also, the description is written from a perspective that every claim is sufficiently enabled.
- Abstract: The complete specification of patent includes an abstract that gives technical information about the invention. Essentially, it’s a summary of the matter in the patent specification. The abstract should not be more than 150 words.
- Claim(s): To say the least, claims section is the most critical part of a patent application. This is because the patentability of an invention is determined by them. Claims clearly lay out the scope of the invention for which protection is sought. Claims should cover important aspects of the invention, such as novelty. This section should be written in a manner to provide the broadest possible coverage and protection for the invention, while remaining novel and non-obvious in light of the existing technologies or art.
- Drawings: A patent specification document also contains drawings that help in aiding the examiner’s understanding of theinvention. Drawings can be diagrams, flowcharts or figures with numeral labeling that identify components or features of the invention described in the claims and detailed description.
Also Read: 4 Best Practices for Background Writing While Drafting a Patent Application
How to Draft Error-free Patent Specifications?
- Avoid Beating Around the Bush: One of the goals while drafting patent specifications is to eliminate ambiguity. As, it poses a challenge during prosecution. The patent drafter must strike a balance between writing information in detail and keeping it specific at the same time.
- Stick to Patent Trademark Office (PTO) Guidelines: Patent offices in various jurisdictions may have their own guidelines for patent drafting. So it is vital to follow them right from the beginning of the drafting process. Additionally, special attention should be given to maintaining the order/sequence of the elements while drafting specifications.
- Seek Professional Assistance: Businesses should never hesitate to seek professional assistance from strategic intellectual property (IP) partners who hold technical and legal prowess in various domains. Furthermore, such IP partners are well-versed with the guidelines of PTOs in various jurisdictions. They provide cost-effective and timely drafting solutions without compromising on quality.
Conclusion
After reading this article, it can be concluded that patent specification is the face of an invention. It helps patent examiners to understand the innovation. That is why drafting the complete specification of patent accurately should be the prime focus of a patent applicant/practitioner. While businesses may choose to work on it by themselves, strategic partners/patent agents make the job relatively easier by helping applicants to prepare a meticulous patent draft that fetches a grant for the invention.
Sagacious IP’s patent drafting solutions are designed to draft accurate and appropriately detailed patent specifications. Also, they are designed to meet the guidelines of the respective patent office. Our patent drafting team ensures that the patent application remains technically sound. Moreover, they ensure it to cover all the possible variations of the invention.
-The Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




