Engineering versus Patent Drawings: Understanding the Difference
Although a simple observation might not reveal much difference between engineering and patent drawings, the actual variations, however, can be quite prominent. Engineering drawings can be defined as rich and specific outlines that show all the detailed information about the product needed for its manufacturing. These drawings, without showing the exact dimensions of the product or item, can be used in the patent application form as patent drawings.
While engineering drawings act as a guide for reproducing the exact product with specific dimensions, patent drawings only highlight the functionality or aesthetics of the product, without any mention of the dimension. So based on the objective, a choice is made between engineering and patent drawings.
This article will discuss the concept of engineering drawings, patent drawings, types of engineering and patent drawings, and finally, the role of both the drawings in patent applications.
Table of Contents
Concept of Engineering Drawings
As mentioned above, the basic concept of engineering drawings is to provide or convey all the information necessary for manufacturing a product. The information includes dimensions, numbers, names of parts, etc. Once the manufacturing team gets the drawing, they can start the production process without a second thought.
Moreover, engineering drawings (as shown in Figure 1) use standardized language and symbols – a common rule for drafting engineering drawings. It makes the drawings simple and easy to understand, with little to no personal interpretation possibilities – since a common rule ensures that understanding of drawing is the same for everyone.
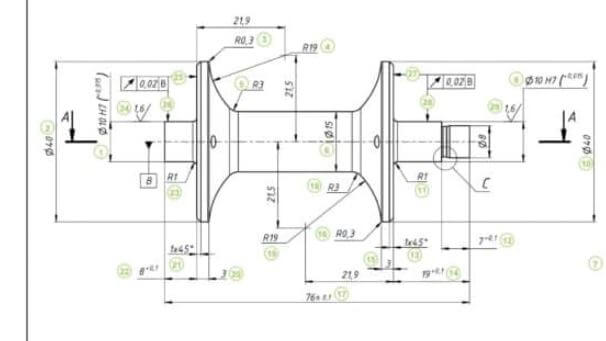
To further enhance your understanding of engineering drawings, it is imperative to delve into the various components of engineering drawings. These are discussed below in detail:
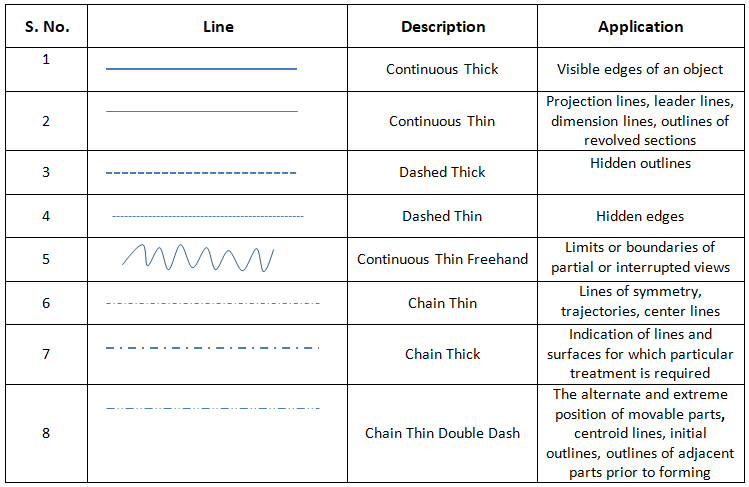
- Different Types of Lines: Every line in engineering drawings represents something different. For instance, continuous lines indicate the boundary of a part or component. In comparison, thicker lines are used to indicate the outer border, and thinner lines are used to reflect inner boundaries. The purpose of hidden lines is to show something that would not be otherwise visible on the drawing. Essentially, it highlights the hidden part or any internal part without a section or a cut-out view. Some of the other lines used are the center line, dimension line, etc. More details about the varied types of lines are discussed in Table 1 below:
2. Different Types of Views: There are primarily two types of views, i.e., isometric views and planer views (a view of an object projected on a horizontal plane), which are further divided into sub views. The different isometric views are front perspective, rear perspective, bottom perspective, etc. The planer views can also be termed as standard views. These are top view, rear view, front view, bottom view, left side view, right side view. Figure 2, shown below, explains the different views.
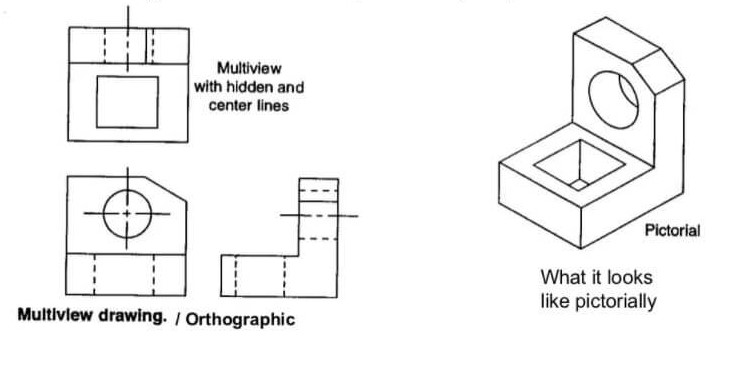
The left side views are planer views, while the image on the right side represents an isometric view.
Often, only images or information of planer views are available. In such cases, with the help of planer views, a 3D image, similar to one on the right-hand side in Figure 2 is prepared. This 3D image is often further used to prepare an object.
After learning the types of views in engineering drawings, it is also essential to understand the different types of engineering drawings. The next section of this article will tell you about these.
Types of Engineering Drawings
There are mainly two types of engineering drawings. These are discussed in detail below:
- Freehand: These drawings are prepared on white paper without using instruments other than pencil and erasers.
2. Instrument drawings: These drawings are prepared using different kinds of modern software, such as AutoCAD.
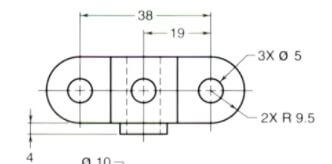
Having understood the two types of engineering drawings, let us now discuss the role of engineering drawings and what they actually do.
Role of Engineering Drawings
- These are used to fully and clearly define the requirements for the engineered items.
- Engineering drawings are used to create standardized conventions for layout, blueprints, nomenclature, interpretation, appearance, size, etc.
- Their purpose is to accurately and unambiguously capture all the geometric features of a product or a component.
- Engineering drawings are used to convey all the required information that will allow a manufacturer to produce the item.
To help you understand the subtle differences between engineering and patent drawings, we will now focus our discussion on patent drawings.
Concept of Patent Drawings
A patent application usually contains drawings used to explain the invention better. Such drawings in a patent application form are referred to as patent drawings. The objective of patent drawings is to illustrate the invention, some of its embodiments (implementations or methods of the invention), or the prior art.
Patent drawings play a vital role in patent applications as they offer a better understanding for the examiner by highlighting the relevant parts of the invention. Therefore, it is often mandatory to use patent drawings in a patent application to convince the examiner and help in expediting the patent grant process. In the absence of patent drawings, there is a greater probability of rejection or an office action (OA).
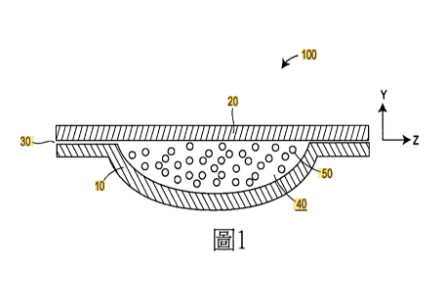
Therefore, professional patent drawings are critical to avoid any rejection and expedite the process of patent examination and approval. In addition, one needs to be meticulous in creating specific and detail-oriented patent drawings as there are particular rules and regulations in place for different patent offices. The additional importance of patent drawings services are shown below in Figure 6:
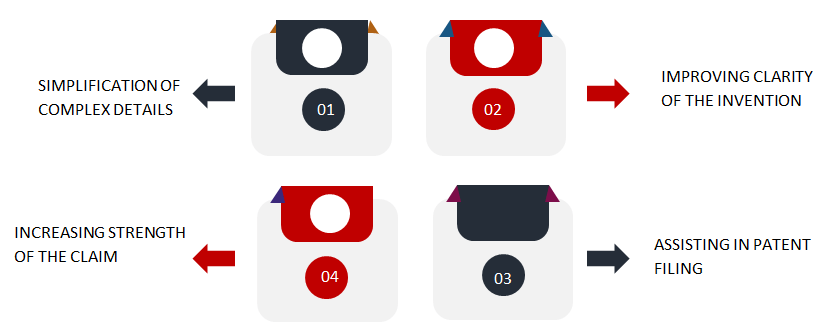
- Simplification of Complex Details: Explaining the working of new machines with several hidden cross-sectional areas can be a daunting task, even for the best of inventors with tons of experience. An examiner or ordinary observer who may not have the required technical prowess will find it challenging to grasp the invention with a textual explanation. That is why patent drawings come in handy to capture the intricate details of the invention more straightforwardly for better clarity. A professional patent illustrator is more adept at placing the drawings in the appropriate place to facilitate easy comprehension for the examiner or a general observer.
- Improving Clarity of the Invention: The description of a new invention that consists of working of complex parts may not be easily grasped by an ordinary observer who lacks the necessary technical knowledge. Patent drawings for various angles can help them visualize the invention’s working in the real world. For example, the working of any mechanical or electronic device is best captured by illustrations to focus on the specific part of the invention.
- Assisting in Patent Filing: While a utility patent is concerned with the feature and functionality, the design patent focuses on the aesthetic part of a product. Design patents are crucial for establishing the uniqueness of a brand, and it is best portrayed with the assistance of a drawing. A well-crafted drawing firmly shows the essence of design and strengthens a brand’s market position.
- Increasing Strength of the Claim: In the absence of neat and well-labeled patent drawings, there is a probability that the claim for the invention might be rejected. The examiner may not understand the invention’s novelty with the textual explanation and deem it unoriginal. Patent drawings that are placed at relevant places aid in boosting the claim of your invention.
After learning about the basic concept of patent drawings, one must also understand the various types of patent drawings and their features.
Types of Patent drawings
There are mainly three types of patent drawings as discussed below:
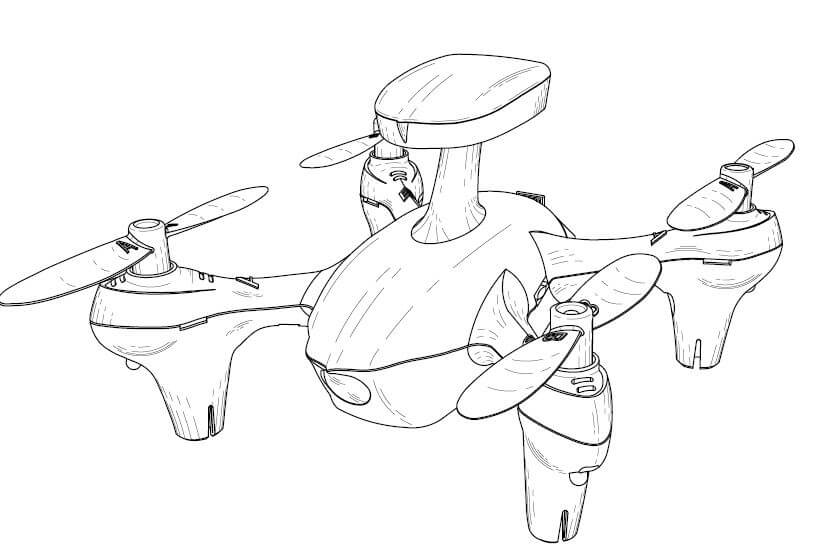
- Utility Patent Drawings: The purpose of utility patents is to protect the product’s functional aspects, i.e., how the article works and how it is used. Utility patent drawings help illustrate the following things – block diagrams, electric circuits, chemical formulas, flow charts, and line drawings showing the shape of objects. In an ideal scenario, the utility patent drawings must cover the entire element mentioned, at least in claims.
Although it is said that the task of preparing utility patent drawings is best left to the professionals, a basic understanding is still necessary for everyone involved. Some of the standards for drafting impeccable utility patent drawings are discussed below:
- Lines Numbers and Figures: The utility patent drawings submitted in patent applications are black and white line drawings with solid and secure black lines. There is more relaxation allowed while filing the provisional applications. Every sheet and figure has to be numbered consecutively, and the text should be at least 1/8 inch in height for better readability upon reduction. The two commonly used sheets sizes for drafting patent drawings are A4 and Letter. The majority of the drafting companies use the default sheet size unless directed to use a specific size.
- Lead Lines: In utility patent drawings, reference numbers are used for correlating a feature to a written description of that feature. To facilitate a better understanding for the examiner, a lead line or other indicator is used to link reference numbers and features. The rule of the thumb regarding lead lines is that they should meet the object, surface, or line identified at a right angle.
- Aesthetics and Improving Legibility: While preparing the utility patent drawings, it is critical to take care of the symmetry. A symmetrical drawing improves the aesthetics and increases its readability and understanding. A utility patent drawing should be easy on the eye so that interpretation of the main points of the drawings becomes easier.
- Flowcharts: Symmetry and consistency are also important while incorporating flow charts for utility patent drawings. The lines and the boxes used in the flowcharts should have the same thickness, color, and size to avoid confusion in the mind of general observers. In addition, the arrow length should be the same to maintain the same distance between two consecutive blocks. A symmetrical and balanced flowchart is successful at delivering the desired message. Figure 7 below shows an example of a utility patent drawing.
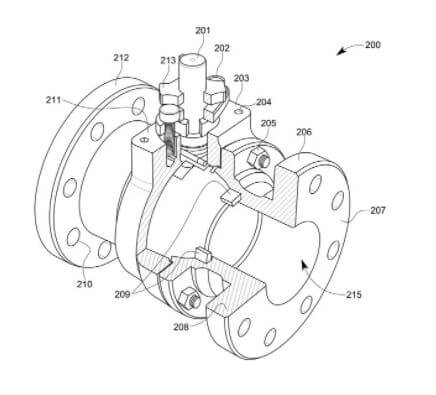
2. Design Patent Drawings: Compared to utility patent drawings, a design patent drawing only protects an article’s ornamental appearance, such as its shape, surface ornamentation, or configuration. It covers the aesthetics of a functional item. Some examples are furniture, jewelry, beverage containers, and computer icons. The shading in design patent drawings must be clear to reflect the invention’s contour, shape, and material textures. Unlike utility patent drawings, design patent drawings do not have reference numbers. Some of the requirements for drafting a clean design patent drawing are listed below:
- Color of Design Patent Drawings: The drawings must be illustrated in black and white. Special care has to be taken for any surface shading to project the character and contour of all surfaces related to the 3D aspect of the design. Broken lines are utilized to indicate portions that are not a part of the claimed design. For special cases, black and white photographs can be used in place of ink drawings if photographs are the only way to illustrate the invention. However, applicants must file a petition and seek approval to file colored drawings or photographs in place of black and white drawings.
- Design Patent Drawings Views: The drawings of the design patent should cover the following views – front, rear, right side, left side, top and bottom. All the views should be presented head-on and not from a particular angle. Views presented from an angle are called perspective views and are not mandatory in patent applications. In case the two views are mirror images of each other, then one of them can be removed. However, it is better to provide a statement confirming that the other side is a mirror image of the one highlighted in the drawing. The bottom view can be omitted if the bottom is flat and has no ornamentation. However, the figure description must include a statement emphasizing the point that the bottom is flat and unornamented. The surfaces that are not flat should not be described as unornamented.
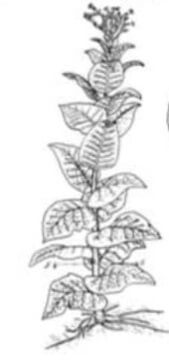
3. Plant Patent Drawings: A plant patent protects the critical features of a plant from being copied or used by others. Plant drawings are generally reproduced in other mediums, such as permanent watercolor renderings that truly capture the appearance of the plant. These drawings are not mechanical in nature and must be well-drafted to highlight their unique characteristics. A large number of inventions are easily understood with the inclusion of patent drawings in patent applications. Plant patent drawings may be in color. However, the color portrayed must also match the respective color designation defined in the color dictionary specification. Usually, two copies of the color drawings are submitted in a patent application.
Having understood the three types of patent drawings and what they entail, let us now discuss the role of patent drawings and where exactly they are used.
Role of Patent Drawings
The most prominent role of patent drawings is to expedite the patent application. In addition, the applications often require patent drawings to help the examiner understand an invention clearly and with minimum effort. This is because patent drawings make a patent application more detailed and illustrative.
There are different patent applications in which patent drawings play a crucial role in understanding the invention more clearly. The various types of applications where a patent drawing is used are discussed below:
- Provisional Application: This is a provisional application filed while the invention is still at the experimentation or development stage. Although the patent application does not need a drawing at this stage, its inclusion does help demonstrate creativity in a more precise way.
- Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) International Application: The PCT applications facilitate patent filing in more than 150 countries using only a single application. Patent drawings are mandatory in this application, while grayscale photographs can be used depending on complexity. However, patent drawings can also be rejected, and the correct drawing should be filed within two months of receiving the office action.
- PCT National Phase Application: An international application can also be filed for a specific country. However, the applicant must file the national phase application within 30 months from the global filing date or priority date, whichever falls earlier. Like PCT international application, patent drawings are compulsory for PCT national phase application. Therefore, patent drawings in the application can be rejected due to lack of novelty and faulty drawings. Sometimes, rejection can be based on hatch patterns used in the drawings that violate USPTO requirements. For instance, the sectional view’s lack of or incorrect hatching can lead to rejection.
- Other Patent Applications: Other types of patent applications that also require patent drawings are typical applications, convention applications, divisional applications, and patent of addition.
With the advancement in technology and readily available software, many organizations perform the task of patent and engineering drawings in-house. However, it is a good idea to explore the services of a reliable third party to avoid office actions and save time. Let us take a look at what sets Sagacious IP apart from other patent drawing service providers.
Why Choose Sagacious IP?
Sagacious IP offers you the best patent drawing services in the industry. We have a team of highly experienced and adept illustrators who specialize in drafting different types of patent drawings. In our patent drawing services, we follow all the rules and regulations of the USPTO to ensure that your patent application is swiftly processed with minimal office actions. With a quick turn-around time and a number of iterations, our team also ensures that customer is delighted with the results.
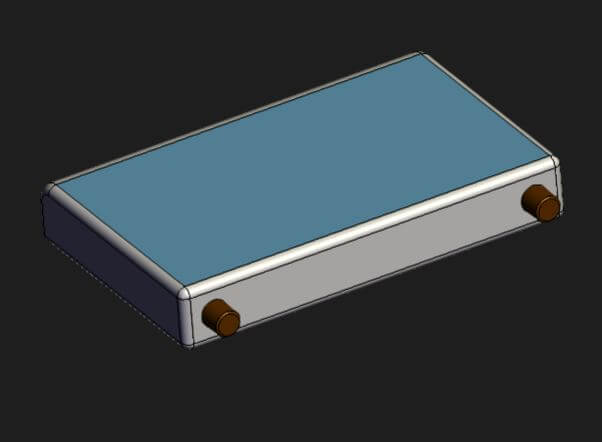
We use the CAD technique for engineering drawings to prepare a solid model in 3D (as shown in Figure 10), which helps generate views with accuracy and precision. The 3D models are designed with the help of experienced illustrators with an engineering background and include all the necessary information for making the final product. Moreover, the team at Sagacious IP can also prepare a 3D model without the exact dimensions with minimum references.
Conclusion
Summing up, we can say that engineering drawings are detailed drawings used to manufacture a product or show a layout like a blueprint with the dimensions of the products. But on the other hand, patent drawings are used in the patent application to demonstrate the invention more clearly. Therefore, hiring the services of a dependable third party becomes critical if you are looking for impeccable patent drawings to save time and expedite the patent application approval process.
Sagacious IP set out to provide next-generation IP solutions for its clients. Over the years, it has formed a team of 300+ techno-legal professionals who have delivered 25,000+ projects across the globe. In addition, through our patent drawings/illustration services, we help prepare patent drawings such as design drawings, utility drawings, plant drawings, trademarks, etc., as per the requirements with the help of our experienced Patent illustrators.
– Rishabh Arora (Illustration) and the Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




