Patent Monetization: A Foolproof Approach to Decide Between Licensing and Selling Patents
Patent monetization is a common practice for companies that possess a sizable portfolio. The methods used for conducting monetization may differ for each one. For instance, a patent owner may decide to turn a patent into a product, enforce it against infringers, or license/sell it. In this article, we talk about the factors one should consider while choosing between monetization methods such as licensing and selling patents. Let us first understand the role of patent monetization and the methods involved.
Table of Contents
Why is Patent Monetization Important?
Companies often rethink and readjust their business strategies to continue generating revenue and prevent losses. This is where patent monetization plays a crucial role as it opens up new streams of revenue inflow in the company. Oftentimes, businesses face difficulty in choosing the right monetization strategy without professional assistance. Strategic guidance by patent practitioners helps them to select the right method as per their business objectives.
There are two widely used patent monetization methods: patent selling and patent licensing. Patent selling involves the transfer of patent ownership to a person or a company for a mutually agreed amount that is received generally as a lump sum. In patent licensing, the patent owner retains the patent right. However, the owner may give exclusive or non-exclusive license in return for royalty payment which is directly related to the sales of the product through licensing.
Factors to be Considered Before Opting for Patent Sales or Licensing
1. How the money rolls in – royalties vs. lump sum
Depending on its needs, a company may choose between a one-time lump sum payment and continuing payments as royalties. If a company is in debt, then it may opt for a lump sum amount. This implies that it can choose to sell. On the other hand, if a company can bear the litigation cost, it might opt for licensing. Read this article to know how one can be benefitted in patent licensing.
2. Core vs. non-core patents
A company’s decision to opt for licensing or sales also depends on the type of patent it wants to monetize – core and non-core. In the case of core patents, it is better to go for patent licensing rather than patent sales.
Considering the factors discussed above, Sagacious IP has developed a proprietary solution known as the F3 analysis model. It assists companies in deciding which patents to license and which ones to sell. In this model, patents in the portfolio are categorized into three subcategories: fundamental patents, future patents and fringe patents. Read our article on this to know more.
According to Sagacious IP’s experience and expertise, one can license both fundamental as well as fringe patents. Licensing fringe patents also prevents counter assertion as one asserts his/her patents on companies that are not direct competitors. Furthermore, the patent owner can even sell his/her fringe patents as it would not result in losing the competitive edge. Figure 1 below encapsulates how patent owners can monetize their patents depending on the category.
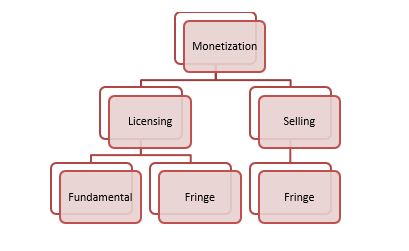
How to Identify Fundamental Patents?
We have observed that big companies categorize their patents. Therefore, by looking at their technology tags, which are related to their business units (BU), one can identify which patents are fundamental. When technology tags are not available, fundamental patents can be identified by CPC codes related to the core businesses or patents which have related features. For instance, let’s assume a company in the mobile domain has a patent related to authentication. Though authentication patent is relevant in multiple fields, it is particularly relevant to the mobile domain. Therefore, this patent is fundamental for the company.
How to Identify Fringe Patents?
Let’s assume a company has a fringe domain (non-core domain) in mind. In this case, it can use search strings to mine patents from the portfolio that are relevant to that domain. Furthermore, it can use CPC analysis to analyze CPC codes of the patent portfolio, analyze tags of the portfolio, and perform citation analysis.
CPC Methodology
CPC methodology is used to quickly identify non-core patents from a large patent portfolio. It saves time since one can simply filter out patents with core CPC to obtain non-core patents and then bucket relevant patents to specific non-core markets/domains.
Despite analyzing fundamental and fringe patents using F3 analysis or CPC code analysis, the ultimate decision of licensing or selling the patent depends on macro analysis. It offers insight into the actual number of potential assets in the portfolio. To do so, one may perform a detailed analysis for each patent, which is very time-consuming. However, Sagacious IP’s approach wherein a detailed analysis is performed on an extremely small subset of patents is both time and cost-effective. Figure 2 illustrates an example of using this approach:
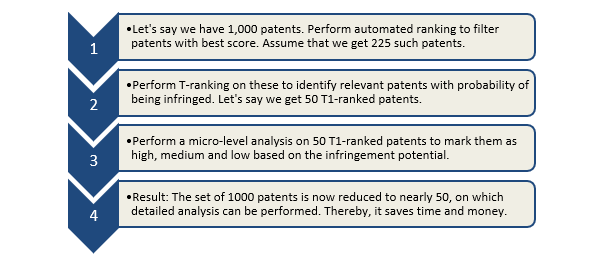
Impact Story
We applied the above-mentioned approach to one of our fortune 100 clients’ portfolio, who initially wanted to enter the payment domain via licensing routes but changed its mind after Sagacious IP’s macro analysis. Read this case study to know more.
How to Assess Value of a Patent Package?
While choosing between licensing or sale of a patent package, it is important to understand the factors involved in determining the asking price of a patent package. The term “asking price” implies that a patent portfolio might be sold at a higher or lower price than what’s actually quoted. Multiple factors are involved in determining the asking price of a patent package such as the average asking price for concerned portfolio technology, size of the package (smaller packages are preferred as they generate more money), alice-affected technology patents in the portfolio, etc.
Conclusion
Patent monetization is a common practice for revenue generation followed by companies that possess sizable portfolios. Licensing and selling patents are the two popular monetization methods that can be used based on specific requirements and objectives. Sagacious IP’s F3 analysis model can help businesses make these strategic decisions and derive quality results.
Sagacious IP’s patent licensing and monetization service provides end-to-end solutions for ranking the patent portfolio and finding potential licensees. The cost-effective solutions offered by us enable companies to transform their IP into a revenue generation unit. Click here to know more about the service and click here to watch a webinar on this subject.
-Aman Goyal (ICT Licensing) and the Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




