Humanoid Robot Related Patents – The Future of Robotic Evolution
The representation of a humanoid robot is not entirely alien to us. Also, sci-fi movies have played a big role in our understanding of such robots. One of the best examples of this can be the movie – Bicentennial Man. Featuring in 1999, this American science fiction drama witnessed the story of Andrew (played by Robin Williams), a humanoid robot, that was capable of feeling emotions.
While the movie gives us a general idea of humanoid robots, there is a lot to its technology than what meets the eye. Moreover, it is a robot that looks like a human being with a few human-like characteristics. Just like humans, it has a torso, a head, two arms and two legs. The design and material of it may vary according to the purpose.
Dr. Nigel Shadbolt (professor at Oxford University) remarked that “we are now entering an age in which children will grow up with robot friends and the elderly will be looked after by robot carers”.
A humanoid robot can be commercially viable and prove to be useful in areas where situations can prove difficult for human beings. They are built to be professional service robots that mimic human motion and interaction. A few examples of such instances would be defense, inspection & maintenance, disaster response, medical and other fields depending upon humanoid’s capabilities.
Table of Contents
Filling Humanoid Robot Related Patents
Now, let us study some of the humanoid robot related patents:
US8511964B2 – The first in the list of humanoid robot related patents discloses a robot that includes a torso, a pair of arms, two hands, a neck, and a head. The torso extends along a primary axis and presents a pair of shoulders. The pair of arms movably extend from the respective shoulder.
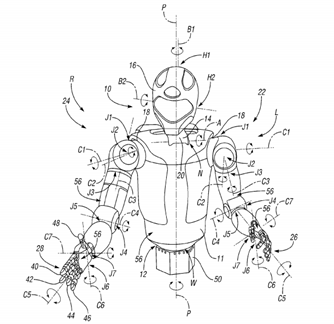
US20120209433A1 – The invention discloses a social robot. The social robot comprises a head in which there is located an artificial vision system made up of webcam cameras, a voice recognition system formed by microphones, and an expression system. The social robot comprises two working wheels for movement.
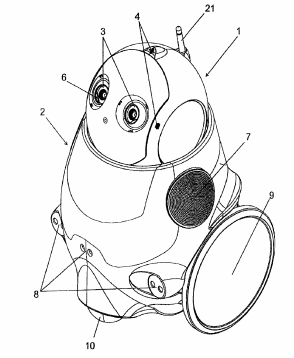
US8676381B2 – The patent discloses a robot that comprises a servo motor in joint for stable walking. The joint comprises a sensor unit for measuring landing information and altitude information of the robot.
A Brief History of Robotics
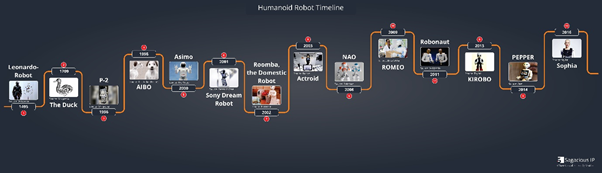
- In 1495 Leonardo da Vinci, sketched a plan for a ‘humanoid robot’ known as Leonardo’s Robot. The robot could stand, sit, wave its arms, raise its visors and move its head while opening and closing its jaw. Pulleys and cables helped the entire robot function. (source)
- In 1927, first World War veteran Captain William Richards, and aircraft engineer Alan Reffell built the first brutish robot (Eric). The robot was operated by two people and voice of Eric was received by a radio signal. He was able to sit and stand. (source)
- In 2000, Honda built the first walking robot ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility). ASIMO had the ability to recognize objects, gestures, surrounding environment, sounds and faces. (source)
- In 2001, Sony also built a Compact robot (height 50cm). It was capable of bipedal motion. It was capable of not only carrying out basic movements, but also balancing itself on one foot and, even, kicking a ball. (Source)
- In 2003, Osaka University developed Actroid, with strong visual human-likeness. It could mimic lifelike functions such as blinking, speaking, and breathing. (Source)
- In 2004, Aldebaran Robotics developed a Nao programmable robot. Nao was a replacement for Sony’s robotic dog , Aibo. Nao played in an international robot soccer competition called the RoboCup Standard Platform League (SPL). (Source)
- In 2016, David Hanson (American roboticist), invented Sophia – the world’s first robot citizen. She is capable of fifty facial expressions and can equally express feelings. Sophia earned the title of the first ever Innovation Champion by the United Nations Development Programme and is also the first non-human. She even got a United Nations title. Moreover, Sophia uses voice recognition technology and is able to get smarter with time!(source)
Building a Humanoid Robot
There are a wide range of tasks in which we can use this robot. To ensure that they are capable to handle various situations, we have to select a suitable material for its design. The following are some of the mechanisms:
- Sensors – To make the robot behave like a human being, sensors play a big role. The use of sensors magnifies the capabilities of these humanoids. The sensors allow robots to perform various intellectual functions just like human beings. There are various sensors that are used in humanoid robots such as Light sensors, Sound Sensor, Temperature Sensor, Contact Sensor, Proximity Sensor, Distance Sensor, Pressure Sensors, Tilt Sensors. For example – in AISMO, the lower portion of the torso has ground sensor which comprises one laser sensor and one infrared sensor. This laser sensor detects the ground surface while the infrared sensor detects pairs of floor markings so that it can confirm the path navigation as per the planned map.
- Actuators – The human body is dynamic and functions according to requirement. We can easily pick up a rock and it can happen in the span of 10 to 15 seconds. To be able to replicate that in robots, we use actuators that perform like muscles and joints, though with a different structure, to achieve the same effect as human motion. Mainly rotary actuators have important role in humanoid robots (Source).
- Controller – Controller is a part of robot that coordinates all motion of the mechanical system in the robot. Controller also receives an input from immediate environment through various sensors. The heart of robot’s controller is a microprocessor that is linked with the input/output and monitoring device. The command issued by the controller activates the motion control mechanism, consisting of various controller, actuators and amplifier. (source)
- Electric motors (DC/AC) – Electric motors help robots in rotational movements. Stepper motors offer accurate positioning without additional encoders. Brushless DC motors are ideal for autonomous function as they drive even at minimal supply voltages. Nowadays electronically commutated DC motors are the best option for long service life and maximum dynamics.
- Power Supply – The working power to the robot is provided by batteries – hydraulic, solar power, or pneumatic power sources.
- Artificial Intelligence- Earlier robots and robotics were restricted with the mechanical and electronic domains only as they were used to enhance mechanical outputs of processes. However, robots are now becoming smarter and more efficient in many ways with the help of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence is like recreation of the human through process that includes the ability to learn, ability to use of a language which makes the humanoid more interactive. For example – if you wanted a robot to open the door, the robot will collect the available data i.e., what kind of latch it is, shape of handle, and feed it to the artificial intelligence which will analyse the data and guide the robot arm to open the door.
How Are They Helpful?
Nowadays, humanoid robots are used as a research tool in several scientific fields. These robots are designated for performing different functions. They are used in inspection, maintenance as well as disaster response ( at power plants) to relieve human workers of laborious and dangerous tasks. Similarly, they are also prepared to take over routine tasks for astronauts in space travel.
Besides research, humanoid robots also perform human tasks such as personal assistance through which they assist the sick and elderly. They are also useful in dangerous jobs that might risk a human life. Humanoids also find relevance in procedurally-based vocations, such as reception-desk administration and replace automotive manufacturing line workers. They can use tools and operate equipment and vehicles designed for humans. For example – Ursula – a female robot can sing, play music, dance as well as speak to her audiences at Universal Studios. There are several Disney theme park shows that use animatronic robots that look like human beings. (Source)

Advanced Humanoid Robots
- Sophia – Sophia is a social robot developed by Hong Kong based company Hanson Robotics that is a unique combination of mechanical, electronics and artificial intelligence. Sophia is a science fiction character, crafted by humans that is depicting the future of artificial intelligence and robotics and serves as a good platform for advance robotics. (source) (US7113848B2)

As mentioned earlier, she is the world’s first robot citizen as well as the first robot innovation ambassador for the United Nations development programme. With her ability of showing over 60 different human expressions, she can easily interact with humans.
- The Actroid (Acting robot) – Developed by the Osaka University, Japan, Actroid is a type of Android robot. It is manufactured by Kokoro Company Ltd. and its first version of android was introduced in 2003. Since then, the android robot has got smarter by using smart sensors and actuators. This makes it more realistic.

- Geminoid F – One of the most popular in the series of humanoid robots built by Hiroshi Ishiguro Laboratories, the Geminoid robot is a look alike of adult women. The new Geminoid F (“F” representing females) is also designed to be remote controlled by a human operator. The android robot can mimic facial expressions of women.

- Romeo – Aldebaran, a French company wanted to develop robots that were able to help the elderly with household tasks and even become their friends. With that in mind, they have developed a robot, known as Romeo. Every movement of Romeo is driven by the maxon’s motors. Romeo looks like a boy and holds a soft appearance to appear friendly. ( US9840009B2)

- Junko Chihira – An ultra-realistic android robot, Junko Chihira is created by the electronic giant – Toshiba. Junko robot does not walk but it can use its arm for gesture and is unable to hold a conversation. She (Junko chihira) can greet customers and visitors. She can speak Japanese, Chinese, English, German, and even sign language.

- Nadine – It was created by the Nanyang Technological University in Singapore. Nadine is a good example of a social robot. Its USP lies in the fact that she is able to memorize conversations. Nadine is working as a customer service agent in AIA Insurance Company in Singapore. This is the first time in the world that such a robot is used as a customer service agent. Source

What The Future Holds for Humanoid Robot Related Patents
A few years ago there was only experimental research on humanoid robotics, whereas now with the faster rate of development, humanoid robots are used in medical, transport and many other fields. Boston consulting group estimates that by 2025 robots will be able to perform 25% of all the labour. This will improve the quality of product and reduce the cost of production. Many countries such as the United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, and the United Kingdom are leading in the way of robot adoption. According to sources they will install 75% of all robotics by 2025. However, researchers are continuously studying human mechanism in order to simplify the interaction between robots and human being. Humanoids will continue to play a significant role in robotics research as it is a futuristic concept and is becoming the greatest potential to become an industrial tool of the future. There are many companies which are working towards creating humanoid robots for the medical field. (Source)
-Brijraj Malav (Engineering) and the Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




