Video Coding and Related Patent Licensing Pools: A Beginner’s Guide
Video technology has evolved significantly over the years, leading to an increase in demand for video content. The increased file size of videos often makes it difficult to ensure quality streaming at high speed. A popular solution to this issue is video encoding which compresses videos to suitable formats, while also facilitating their transmission without compromising on quality. In order to promote innovation in this field and to ensure equitable access to such technologies for all, licensing pools are created.
The following article discusses video coding, streaming technologies, video coding standards, and why video codec patent licensing pools are important.
Table of Contents
Defining Video Encoding
Before we begin discussing video coding standards or streaming technologies, let us first understand video encoding.
Video encoding is the process of converting raw video data into a digital format that is compatible with multiple devices. Such a conversion can be done with the help of a video codec – a device/program that reduces the size of a digital data file to a manageable one, thereby making its storage and distribution easier. A codec has two components – an encoder and a decoder. The encoder helps in compressing raw video files while the decoder recreates the final video for playback. Below is an illustration of how encoders and decoders work in video encoding:
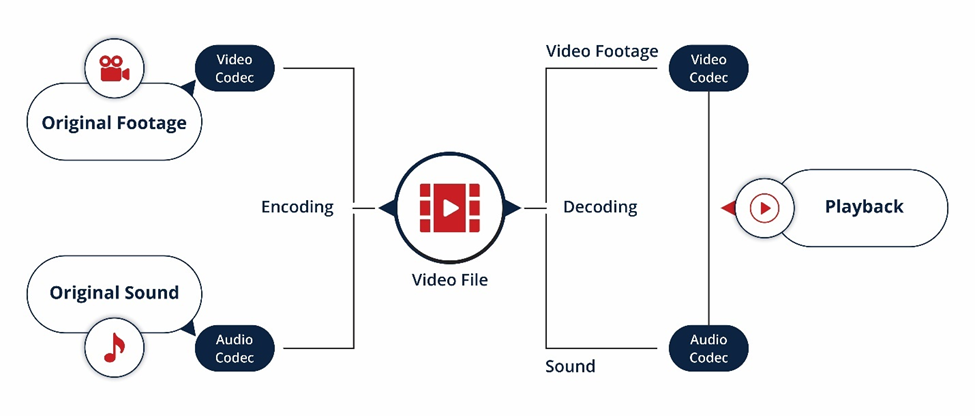
Role of Video Coding Standards and Streaming Technologies in Video Transmission
A video coding standard is a document that explains a bitstream structure as well as the decoding method for compression of videos. Such a standard is essential for understanding the video coding process. At present, multiple video coding standards are available in the market including VP9, H.266/Versatile Video Coding (VVC), AOMedia Video 1 (AV1), H.265/High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), and H.264/Advanced Video Coding (AVC).
Besides the video coding standards, streaming technologies are also crucial as they help in sharing compressed videos to the end devices/users. Some of the popular video streaming standards/protocols include Motion Picture Experts Group-Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH) and HTTP live streaming (HLS). These standards break the video into chunks, send the chunks to the end device, and then reassemble the data to make it playable. The image below represents the overall architecture of a video distribution network including video codecs and streaming protocols.
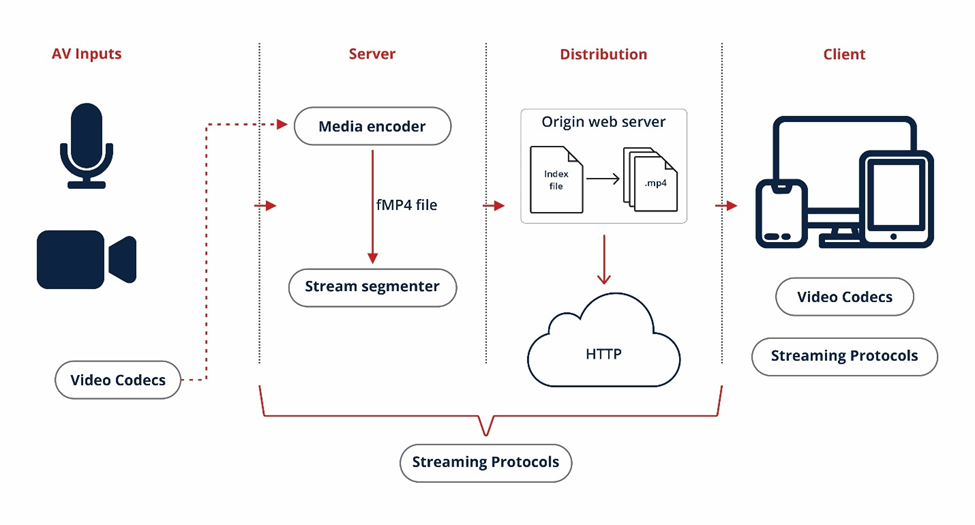
Standard Setting Organizations for Video Codecs
By definition, a standard-setting organization(SSO) develops and adopts an industry standard for a particular domain. Two standard-setting organizations – the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) have developed a series of standards that have shaped the media industry. The ISO has created the Motion Picture Experts Group (MPEG) series of standards such as MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4. While the ITU has published the H.26x line of coding standards including H.261, H.262, H.263, H.264, H.265, and H.266 (the VVC standard).
Video Codec Patent Licensing Pools and their Importance
When competing businesses with patents on a specific technology refuse to share their IP, it dampens innovation in that industry. One way to tackle this issue is to create a patent pool, which is an agreement between two or more patent holders who transfer their IP to a joint venture. The businesses inside the pool either enter into a cross-license agreement with each other or with a third party. Such a pool enables licensees to use patents on fair, reasonable, and non-discriminatory (FRAND) terms.
When it comes to video codecs, there are three main patent pool administrators – HEVC Advance, MPEG LA, and Velos Media. HEVC Advance (also known as Access Advance) has been created to develop, administer, and manage patent pools related to HEVC or H.265 standards. This patent pool administrator recently launched the VVC/H.266 pool and also introduced a multi-codec bridging agreement (MCBA). MPEG LA has also announced the development of a VVC standard patent licensing pool. Velos Media is yet another independent company licensing standard patents from different companies. While these pools allow licensees access to as many patents as possible, there is a probability of some patents being essential to the standards but not being part of any of these pools. The best way to tackle this challenge is to have an all-inclusive patent pool.
Conclusion
Given the growing video viewership around the world, it is imperative to provide quality videos at high speed. Video coding and streaming technologies can help in doing so by compressing videos and transmitting them while maintaining their quality. Further, to foster innovation in the media industry and ensure equitable access to these programs or technologies and their related patents, some licensing pools have been created. However, there is an increasing need to fine-tune how FRAND licensing is being done by these pools due to the high disparity in their royalty rates. To know more about the topic, view our webinar here.
- Abhinav Mahajan, Gagandeep Singh (ICT Licensing) and the Editorial Team
Having Queries? Contact Us Now!
"*" indicates required fields




